Bibcode
Efstathiou, Andreas; Małek, Katarzyna; Burgarella, Denis; Hurley, Peter; Oliver, Seb; Buat, Veronique; Shirley, Raphael; Duivenvoorden, Steven; Lesta, Vicky Papadopoulou; Farrah, Duncan; Duncan, Kenneth J.; Varillas, María del Carmen Campos
Referencia bibliográfica
Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society
Fecha de publicación:
5
2021
Número de citas
15
Número de citas referidas
15
Descripción
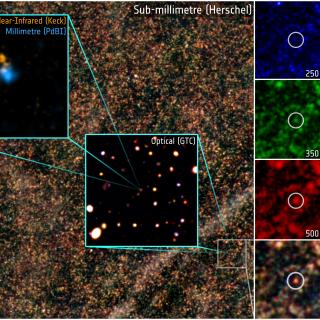
In this work we report the discovery of the hyperluminous galaxy HELP_J100156.75 + 022344.7 at a photometric redshift of $z$ ≍ 4.3. The galaxy was discovered in the Cosmological Evolution Survey (COSMOS) field, one of the fields studied by the Herschel Extragalactic Legacy Project (HELP). We present the spectral energy distribution (SED) of the galaxy and fit it with the CYprus models for Galaxies and their NUclear Spectra (CYGNUS) multi-component radiative transfer models. We find that its emission is dominated by an obscured quasar with a predicted total 1-1000 μm luminosity of $3.91^{+1.69}_{-0.55} \times 10^{13}\, \mathrm{ L}_\odot$ and an active galactic nucleus (AGN) fraction of $\sim 89{{\ \rm per\ cent}}$ . We also fit HELP_J100156.75 + 022344.7 with the CIGALE(Code Investigating GALaxy Emission) code and find a similar result. This is only the second $z$ > 4 hyperluminous obscured quasar discovered to date. The discovery of HELP_J100156.75 + 022344.7 in the ∼2 deg2 COSMOS field implies that a large number of obscured hyperluminous quasars may lie in the HELP fields, which cover ∼1300 deg2. If this is confirmed, tension between supermassive black hole evolution models and observations will be alleviated. We estimate the space density of objects like HELP_J100156.75 + 022344.7 at $z$ ≍ 4.5 to be ∼1.8 × 10-8 Mpc-3. This is slightly higher than the space density of coeval hyperluminous optically selected quasars, suggesting that the obscuring torus in $z$ > 4 quasars may have a covering factor $\gtrsim 50{{\ \rm per\ cent}}$ .
Proyectos relacionados
Formación y Evolución de Galaxias: Observaciones Infrarrojas y en otras Longitudes de Onda
Este grupo desarrolla varios proyectos extragalácticos en diferentes rangos del espectro electromagnético utilizando satélites y telescopios en tierra para estudiar la evolución cosmológica de las galaxias y el origen de la actividad nuclear en galaxias activas. En el aspecto instrumental, el grupo forma parte del consorcio internacional que ha
Ismael
Pérez Fournon