General
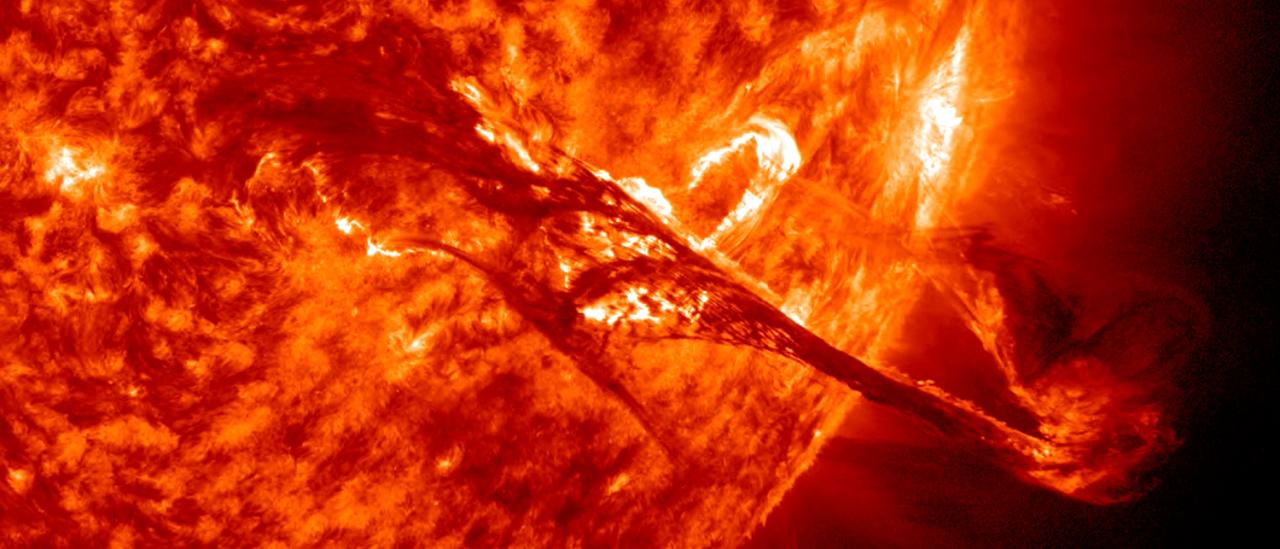
Magnetic fields are at the base of star formation and stellar structure and evolution. When stars are born, magnetic fields brake the rotation during the collapse of the mollecular cloud. In the end of the life of a star, magnetic fields can play a key role in the form of the strong winds that lead to the last stages of stellar evolution. During the whole adult life of a star, magnetic fields are the origin of stellar activity. Our Sun has magnetic fields that give rise to such spectacular activity that impacts the climate on Earth. The magnetic activity in other stars is, in some cases, of orders of magnitude more intense than the solar one, influencing – often drastically – the transport of chemical species and angular momentum, as well as affecting the possible planetary systems around them.
The aim of this project is the study of the diverse manifestations of the magnetic field that can be observed in the solar atmosphere and in other stars. These include distinct structures as sunspots, weak quiet-sun fields or chromospheric and coronal features such as filaments and prominences. The following research topics have been gradually faced:
Solar magnetism
1. Structure and evolution of Sunspot magnetic fields.
2. Structure and evolution of quiet Sun magnetic fields.
3. Structure and evolution of the magnetism of the chromosphere and of chromospheric strcutures (promiences, spicules,...)
4. Structure and evolution or coronal loops.
5. Structure and evolution of the Sun's global field. Studies of the activity cycle.
6. Empirical study of propagation of magnetohydrodynamic waves in magnetic structures.
7. Empirical study of energy transfer mechanisms related with the heating of the external atmospheric layers.
8. Empirical study of the influence of partial ionisation in the dynamics of the solar atmosphere.
9. Participation in the European Solar Telescope project.
Stellar magnetism
1. Development of numerical tools to diagnose stellar magnetic fields, both in the surface and in the chromsphere.
2. Study of magnetic fields in stellar prominences.
3. Study of the role of magnetic fields in the late stages of stellar evolution.
Members
Results
- Spiral waves in sunspots: They have been interpreted as magnetoacoustic waves propagating from the interior to the atmosphere following the direction of the magnetic field. We have characterized the magnetic field topology, dismissing the twist of the field lines as the cause of the spiral shape (Felipe et al. 2019).
- Magnetic response to umbral flashes: Simultaneous spectropolarimetric observations of the chromospheric He I 10830 and Ca II 8542 lines have been used to estimate the fluctuations of the magnetic field associated to shock waves. The shocks cause expansion of the magnetic field lines (Houston et al. 2018, including A. Asensio Ramos).