Astronomical seeing (units arcesec) refers to the blurring or instantaneous image broadening of astronomical objects caused by turbulent mixing in the Earth's atmosphere due to the variations of the optical refractive index.
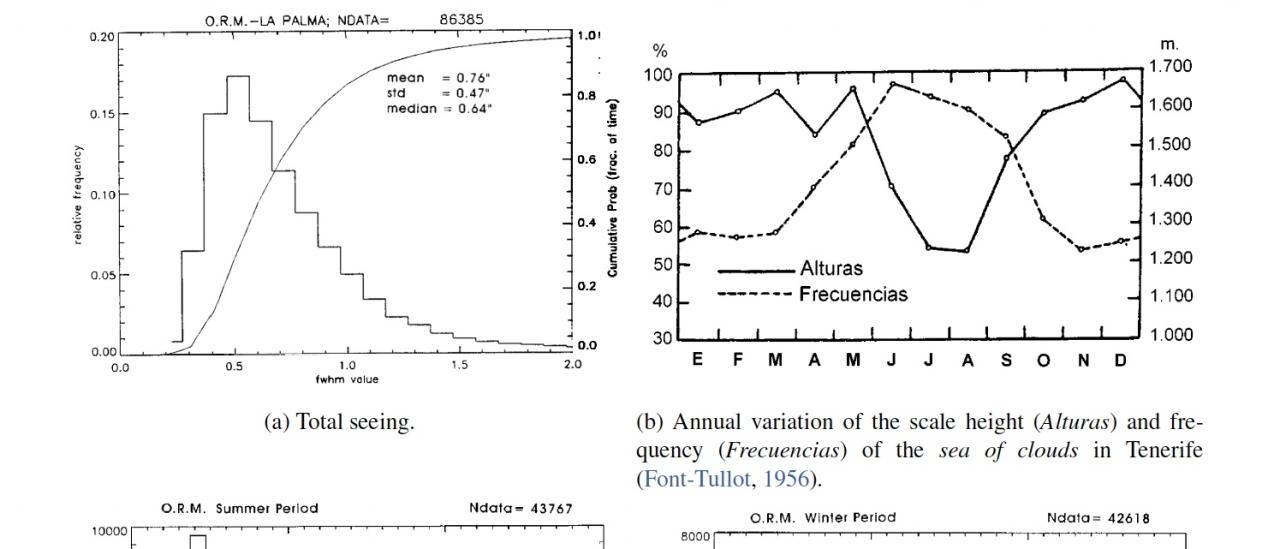
Atmospheric optical conditions are crucial for selecting the best astronomical sites of the world, among them, the seeing because is directly related with the spatial resolution of images. Typical median seeing at the Canarian Observatories is of 0.7".
The differential image motion monitor (Stock & Keller 1960; Sarazin & Roddier 1990; Vernin & Muñoz-Tuñón 1995) oper- ates by measuring the wavefront slope differences over two small pupils some distance apart.
The seeing values at the ORM ranges from 0.63" to 0.72" (25th perc.=0.53"). Thes values, well below 1", assure the optimal conditions for High Resolution and AO in particular. The results obtained with different techniques and periods, are all in very good agreement with differences below one tenth.