Bibcode
Delabrouille, J.; Démoclès, J.; Désert, F.-X.; de Bernardis, P.; de Gasperis, G.; de Zotti, G.; Cuttaia, F.; Da Silva, A.; Dahle, H.; Danese, L.; Davis, R. J.; Coulais, A.; Crill, B. P.; Colombo, L. P. L.; Comis, B.; Clements, D. L.; Colafrancesco, S.; Colombi, S.; Chiang, L.-Y.; Chon, G.; Christensen, P. R.; Churazov, E.; Cayón, L.; Chamballu, A.; Carvalho, P.; Castex, G.; Catalano, A.; Cabella, P.; Cardoso, J.-F.; Burenin, R.; Burigana, C.; Bourdin, H.; Brown, M. L.; Borgani, S.; Borrill, J.; Bouchet, F. R.; Bonaldi, A.; Bond, J. R.; Bikmaev, I.; Bobin, J.; Böhringer, H.; Bersanelli, M.; Bhatia, R.; Benoît, A.; Bernard, J.-P.; Battaner, E.; Benabed, K.; Barreiro, R. B.; Bartlett, J. G.; Baccigalupi, C.; Balbi, A.; Banday, A. J.; Atrio-Barandela, F.; Aumont, J.; Arnaud, M.; Ashdown, M.; Ade, P. A. R.; Aghanim, N.; Hempel, A.; Henrot-Versillé, S.; Hernández-Monteagudo, C.; Herranz, D.; Hildebrandt, S. R.; Hivon, E.; Hobson, M.; Holmes, W. A.; Hurier, G.; Jaffe, T. R.; Jaffe, A. H.; Jagemann, T.; Jones, W. C.; Juvela, M.; Keihänen, E.; Khamitov, I.; Kisner, T. S.; Kneissl, R.; Knoche, J.; Knox, L.; Kunz, M.; Kurki-Suonio, H.; Lagache, G.; Lähteenmäki, A.; Lamarre, J.-M.; Lasenby, A.; Lawrence, C. R.; Le Jeune, M.; Leonardi, R.; Liddle, A.; Lilje, P. B.; López-Caniego, M.; Luzzi, G.; Macías-Pérez, J. F.; Maino, D.; Mandolesi, N.; Maris, M.; Marleau, F.; Marshall, D. J.; Martínez-González, E.; Masi, S.; Massardi, M. et al.
Referencia bibliográfica
Astronomy and Astrophysics, Volume 550, id.A131, 24 pp.
Fecha de publicación:
2
2013
Revista
Número de citas
318
Número de citas referidas
300
Descripción
Taking advantage of the all-sky coverage and broadfrequency range of the
Planck satellite, we study the Sunyaev-Zeldovich (SZ) and pressure
profiles of 62 nearby massive clusters detected at high significance in
the 14-month nominal survey. Careful reconstruction of the SZ signal
indicates that most clusters are individually detected at least out to
R500. By stacking the radial profiles, we have statistically
detected the radial SZ signal out to 3 × R500, i.e., at
a density contrast of about 50-100, though the dispersion about the mean
profile dominates the statistical errors across the whole radial range.
Our measurement is fully consistent with previous Planck results on
integrated SZ fluxes, further strengthening the agreement between SZ and
X-ray measurements inside R500. Correcting for the effects of
the Planck beam, we have calculated the corresponding pressure profiles.
This new constraint from SZ measurements is consistent with the X-ray
constraints from XMM-Newton in the region in which the profiles overlap
(i.e., [0.1-1] R500), and is in fairly good agreement with
theoretical predictions within the expected dispersion. At larger radii
the average pressure profile is slightly flatter than most predictions
from numerical simulations. Combining the SZ and X-ray observed profiles
into a joint fit to a generalised pressure profile gives best-fit
parameters [P0,c500,γ,α,β ] =
[6.41,1.81,0.31,1.33,4.13 ] . Using a reasonable hypothesis for the gas
temperature in the cluster outskirts we reconstruct from our stacked
pressure profile the gas mass fraction profile out to 3 R500.
Within the temperature driven uncertainties, our Planck constraints are
compatible with the cosmic baryon fraction and expected gas fraction in
halos.
Appendices are available in electronic form at http://www.aanda.org
Proyectos relacionados
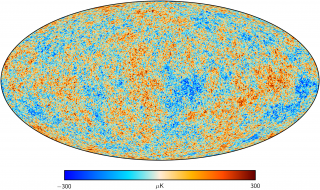
Anisotropía del Fondo Cósmico de Microondas
El objetivo general de este proyecto es determinar y estudiar las variaciones espaciales y espectrales en la temperatura del Fondo Cósmico de Microondas y en su Polarización en un amplio rango de escalas angulares que van desde pocos minutos de arco hasta varios grados. Las fluctuaciones primordiales en la densidad de materia, que dieron origen a
Rafael
Rebolo López
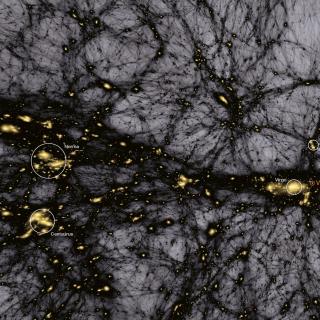
Cosmología con Trazadores de la Estructura a Gran Escala del Universo
El Fondo Cósmico de Microondas (FCM) contiene la información estadística de las semillas primigenias que han dado lugar a la formación de todas las estructuras en el Universo. Su contrapartida natural en el Universo local es la distribución de las galaxias que surgen como resultado del crecimiento gravitatorio de aquellas fluctuaciones de densidad
FRANCISCO SHU
KITAURA JOYANES