Bibcode
Chen, A.; Aricò, G.; Huterer, D.; Angulo, R. E.; Weaverdyck, N.; Friedrich, O.; Secco, L. F.; Hernández-Monteagudo, C.; Alarcon, A.; Alves, O.; Amon, A.; Andrade-Oliveira, F.; Baxter, E.; Bechtol, K.; Becker, M. R.; Bernstein, G. M.; Blazek, J.; Brandao-Souza, A.; Bridle, S. L.; Camacho, H.; Campos, A.; Carnero Rosell, A.; Carrasco Kind, M.; Cawthon, R.; Chang, C.; Chen, R.; Chintalapati, P.; Choi, A.; Cordero, J.; Crocce, M.; Pereira, M. E. S.; Davis, C.; DeRose, J.; Di Valentino, E.; Diehl, H. T.; Dodelson, S.; Doux, C.; Drlica-Wagner, A.; Eckert, K.; Eifler, T. F.; Elsner, F.; Elvin-Poole, J.; Everett, S.; Fang, X.; Ferté, A.; Fosalba, P.; Gatti, M.; Gaztanaga, E.; Giannini, G.; Gruen, D.; Gruendl, R. A.; Harrison, I.; Hartley, W. G.; Herner, K.; Hoffmann, K.; Huang, H.; Huff, E. M.; Jain, B.; Jarvis, M.; Jeffrey, N.; Kacprzak, T.; Krause, E.; Kuropatkin, N.; Leget, P. -F.; Lemos, P.; Liddle, A. R.; MacCrann, N.; McCullough, J.; Muir, J.; Myles, J.; Navarro-Alsina, A.; Omori, Y.; Pandey, S.; Park, Y.; Porredon, A.; Prat, J.; Raveri, M.; Refregier, A.; Rollins, R. P.; Roodman, A.; Rosenfeld, R.; Ross, A. J.; Rykoff, E. S.; Samuroff, S.; Sánchez, C.; Sanchez, J.; Sevilla-Noarbe, I.; Sheldon, E.; Shin, T.; Troja, A.; Troxel, M. A.; Tutusaus, I.; Varga, T. N.; Wechsler, R. H.; Yanny, B.; Yin, B.; Zhang, Y.; Zuntz, J.; Aguena, M.; Annis, J. et al.
Referencia bibliográfica
Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society
Fecha de publicación:
2
2023
Número de citas
52
Número de citas referidas
44
Descripción
We use the small scales of the Dark Energy Survey (DES) Year-3 cosmic shear measurements, which are excluded from the DES Year-3 cosmological analysis, to constrain the baryonic feedback. To model the baryonic feedback, we adopt a baryonic correction model and use the numerical package BACCOEMU to accelerate the evaluation of the baryonic non-linear matter power spectrum. We design our analysis pipeline to focus on the constraints of the baryonic suppression effects, utilizing the implication given by a principal component analysis on the Fisher forecasts. Our constraint on the baryonic effects can then be used to better model and ameliorate the effects of baryons in producing cosmological constraints from the next-generation large-scale structure surveys. We detect the baryonic suppression on the cosmic shear measurements with a ~2σ significance. The characteristic halo mass for which half of the gas is ejected by baryonic feedback is constrained to be $M_c \gt 10^{13.2} \, h^{-1} \, \mathrm{M}_{\odot }$ (95 per cent C.L.). The best-fitting baryonic suppression is $\sim 5{{\ \rm per\ cent}}$ at $k=1.0 \, {\rm Mpc}\ h^{-1}$ and $\sim 15{{\ \rm per\ cent}}$ at $k=5.0 \, {\rm Mpc} \ h^{-1}$. Our findings are robust with respect to the assumptions about the cosmological parameters, specifics of the baryonic model, and intrinsic alignments.
Proyectos relacionados
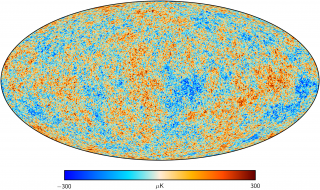
Anisotropía del Fondo Cósmico de Microondas
El objetivo general de este proyecto es determinar y estudiar las variaciones espaciales y espectrales en la temperatura del Fondo Cósmico de Microondas y en su Polarización en un amplio rango de escalas angulares que van desde pocos minutos de arco hasta varios grados. Las fluctuaciones primordiales en la densidad de materia, que dieron origen a
Rafael
Rebolo López
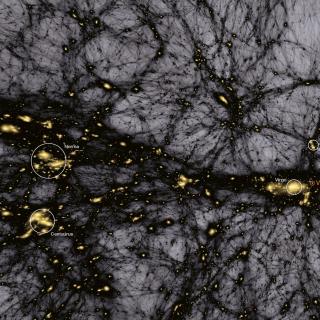
Cosmología con Trazadores de la Estructura a Gran Escala del Universo
El Fondo Cósmico de Microondas (FCM) contiene la información estadística de las semillas primigenias que han dado lugar a la formación de todas las estructuras en el Universo. Su contrapartida natural en el Universo local es la distribución de las galaxias que surgen como resultado del crecimiento gravitatorio de aquellas fluctuaciones de densidad
FRANCISCO SHU
KITAURA JOYANES