Bibcode
Færder, Ø. H.; Nóbrega-Siverio, D.; Carlsson, M.
Referencia bibliográfica
Astronomy and Astrophysics
Fecha de publicación:
3
2024
Revista
Número de citas
7
Número de citas referidas
6
Descripción
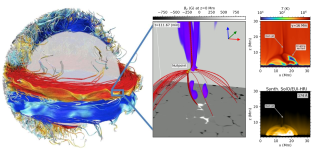
Context. Plasmoid-mediated reconnection plays a fundamental role in different solar atmospheric phenomena. Numerical reproduction of this process is therefore essential for developing robust solar models.
Aims: Our goal is to assess plasmoid-mediated reconnection across various numerical resistivity models in order to investigate how plasmoid numbers and reconnection rates depend on the Lundquist number.
Methods: We used the Bifrost code to drive magnetic reconnection in a 2D coronal fan-spine topology, carrying out a parametric study of several experiments with different numerical resolution and resistivity models. We employed three anomalous resistivity models: (1) the original hyper-diffusion from Bifrost, (2) a resistivity proportional to current density, and (3) a resistivity quadratically proportional to electron drift velocity. For comparisons, experiments with uniform resistivity were also run.
Results: Plasmoid-mediated reconnection is obtained in most of the experiments. With uniform resistivity, increasing the resolution reveals higher plasmoid frequency with weaker scaling to the Lundquist number, obtaining 7.9-12 plasmoids per minute for SL ∈ [1.8 × 104, 2.6 × 105] with a scaling of SL0.210 in the highest-resolution resistivity cases, transcending into Petschek reconnection in the high-SL limit (where the diffusive effects of the resistivity become small compared to the non-uniform viscosity) and Sweet-Parker reconnection in the low-SL limit. Anomalous resistivity leads to similar results even with lower resolution. The drift-velocity-dependent resistivity excellently reproduces Petschek reconnection for any Lundquist number, and similar results are seen with resistivity proportional to current-density though with slightly lower reconnection rates and plasmoid numbers. Among the different resistivity models applied on the given numerical resolution, the hyper-diffusion model reproduced plasmoid characteristics in closest resemblance to those obtained with uniform resistivity at a significantly higher resolution.
Aims: Our goal is to assess plasmoid-mediated reconnection across various numerical resistivity models in order to investigate how plasmoid numbers and reconnection rates depend on the Lundquist number.
Methods: We used the Bifrost code to drive magnetic reconnection in a 2D coronal fan-spine topology, carrying out a parametric study of several experiments with different numerical resolution and resistivity models. We employed three anomalous resistivity models: (1) the original hyper-diffusion from Bifrost, (2) a resistivity proportional to current density, and (3) a resistivity quadratically proportional to electron drift velocity. For comparisons, experiments with uniform resistivity were also run.
Results: Plasmoid-mediated reconnection is obtained in most of the experiments. With uniform resistivity, increasing the resolution reveals higher plasmoid frequency with weaker scaling to the Lundquist number, obtaining 7.9-12 plasmoids per minute for SL ∈ [1.8 × 104, 2.6 × 105] with a scaling of SL0.210 in the highest-resolution resistivity cases, transcending into Petschek reconnection in the high-SL limit (where the diffusive effects of the resistivity become small compared to the non-uniform viscosity) and Sweet-Parker reconnection in the low-SL limit. Anomalous resistivity leads to similar results even with lower resolution. The drift-velocity-dependent resistivity excellently reproduces Petschek reconnection for any Lundquist number, and similar results are seen with resistivity proportional to current-density though with slightly lower reconnection rates and plasmoid numbers. Among the different resistivity models applied on the given numerical resolution, the hyper-diffusion model reproduced plasmoid characteristics in closest resemblance to those obtained with uniform resistivity at a significantly higher resolution.
Movies are available at https://www.aanda.org.
Proyectos relacionados
El proyecto Whole Sun: desentrañando los complejos mecanismos físicos detrás de nuestra estrella eruptiva y sus gemelos
El Sol es una estrella activa magnéticamente cuyas erupciones violentas pueden impactar y deformar la magnetosfera terrestre y causar perturbaciones importantes en instalaciones tecnológicas en tierra y en órbita. The Whole Sun tiene como objetivo central abordar, de forma coherente y por primera vez, cuestiones actuales clave en Física Solar
Fernando
Moreno Insertis
Simulación Numérica de Procesos Astrofísicos
La simulación numérica mediante códigos complejos de ordenador es una herramienta fundamental en la investigación física y en la técnica desde hace décadas. El crecimiento vertiginoso de las capacidades informáticas junto con el avance notable de la matemática numérica ha hecho accesible a los centros de investigación de tamaño medio
Daniel Elías
Nóbrega Siverio