Related grants:
General
Starsbursts play a key role in the cosmic evolution of galaxies, and thus in the star formation (SF) history of the universe, the production of metals, and the feedback coupling galaxies with the cosmic web. Extreme SF conditions prevail early on during the formation of the first stars and galaxies, therefore, the starburst phenomenon constitutes a fundamental ingredient of our understanding of the Universe. Starbursts are observed throughout, from the giant HII regions in nearby spirals, to the massive clumps typical of high redshift objects. This project is aimed at carrying out a comprehensive study of the physics of local massive SF regions in order to enlarge our understanding of the most distant galaxies and most extreme starbursts. We combine observational studies (using ground-based and space-borne spectrophotometry) along with our self-consistent theoretical models. Among the observational facilities, the team is directly involved in the development and scientific exploitation of the GTC instruments EMIR and MEGARA, which will become operational during the timespan of the project.
We have structured our research for the next three years around five main objectives:
1) The interplay between massive SF and the interstellar medium within galaxies.
2) Understanding the formation of disk galaxies.
3) The role of the environment on massive SF and the evolution of galaxies.
4) Extreme starbursting in the early Universe.
5) Participation in the science verification and building of new instrumentation.
The main results expected from this project include: i) constraining the chemical evolution of galaxies using a combination of integral-field spectroscopy and fully bi-dimensional models, ii) understanding the role of molecular gas and high-energy background photons on the formation of galaxies, iii) developing a technique to image the cosmic web gas that feeds the starbursts, iv) characterizing the chemical and dynamical properties of the gas that is falling into the galaxies, v) deciphering the different ways in which the environment can affect the SF in star-forming galaxies along cosmic time; paying special attention to the triggering of violent SF bursts in the lowest metallicity galaxies. vi) explaining how very massive and compact starbursts may evolve in the so-called positive feedback mode, accounting for extreme starbursts in local galaxy analogs to the objects present in the primeval universe. vii) understanding the SF in Lya and Ly-break galaxies, viii) constraining the existence of candidate stars analog to PopIII in extremely metal-poor galaxies, both in the local universe and at high redshift, ix) developing the know-how needed for effective use of EMIR and MEGARA. We aim at getting the most from these new instruments by leading science cases during verification phase and later on.
Members
Results
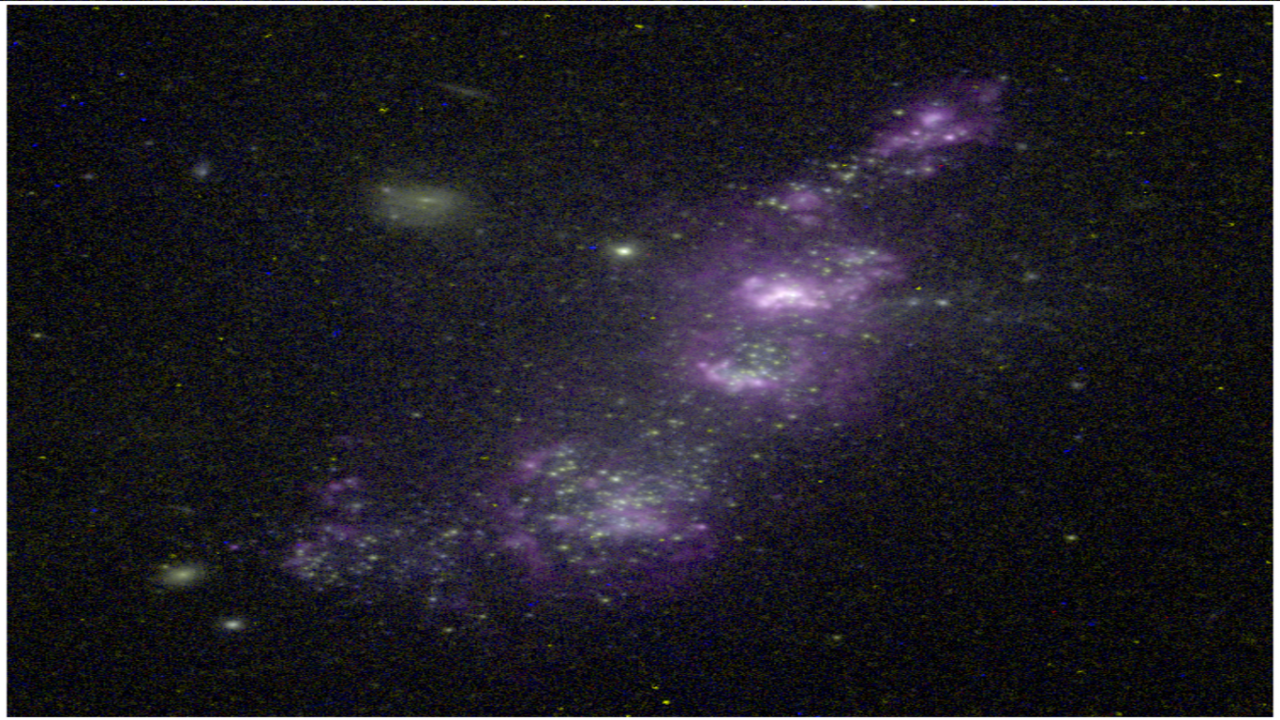
- Local anticorrelation between star formation rate and gas-phase metallicity in disc galaxies Using a representative sample of 14 star-forming dwarf galaxies in the local Universe, we show the existence of a spaxel-to-spaxel anticorrelation between the index N2 ≡ log ([N II]λ 6583/H α ) and the H α flux.
- Discovery of a high-metallicity low mass galaxy, confirming the stochasticity of the cosmic web gas feed star formation
- Pyroclastic Blowout: Dust Survival in Supernovi Events
- A simultaneous search for high-z LAEs and LBGs in the SHARDS survey.We derive redshifts, star formation rates, Lyα equivalent widths, and luminosity functions (LFs). Grouping within our sample is also studied, finding 92 pairs or small groups of galaxies
- A possible binary AGN has been found in Mrk 622.