General
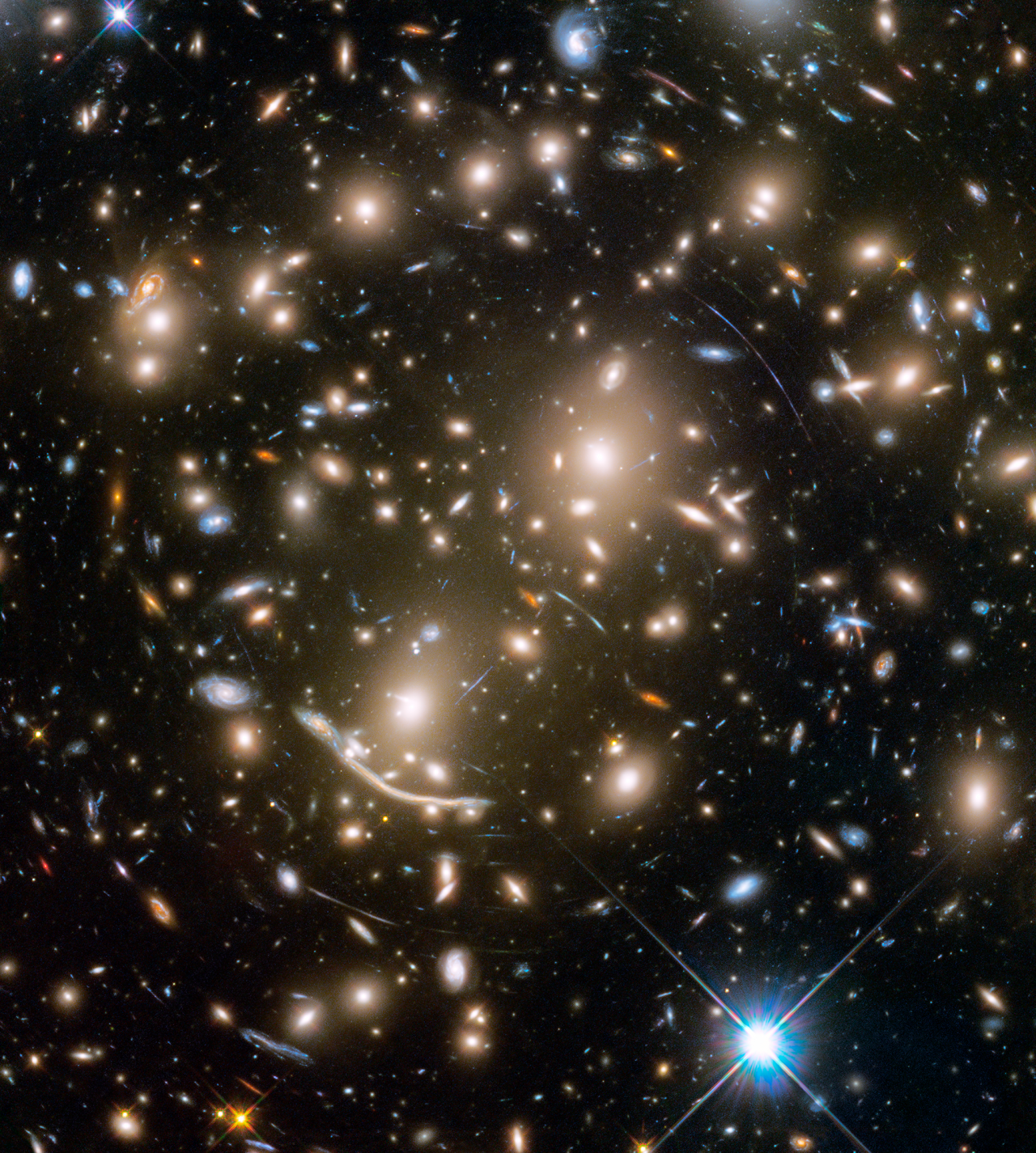
Galaxies in the universe can be located in different environments, some of them are isolated or in low density regions and they are usually called field galaxies. The others can be located in galaxy associations, going from loose groups to clusters or even superclusters of galaxies. One of the foremost challenges of the modern Astrophysics is to achieve a complete theory about galaxy evolution. This theory should explain the relation between the environment and galaxy evolution. Galaxy clusters are high density environments where galaxies interact one to each other and with the intracluster material (ICM). In addition, the cluster dynamics is driven by the high density and quantity of dark matter present in them. Therefore, galaxy clusters are complex systems with multiple components (galaxies, ICM, dark matter) which are tightly bounded. The mix of all these components, as well as their interactions, makes galaxy clusters ideal laboratories to study the different mechanisms which cause the different evolution of galaxies in this high density environments with respect to field galaxies.
The objective of this project is to study the formation and evolution of galaxies in these dense environments. The ‘Galaxy Evolution in Clusters’ group intend to understand in what environment each of the mechanisms proposed by numerical simulations to transform the galaxies dominates and how the evolution of the different types of galaxies (both bright and dwarf) occurs in the clusters. Quantifying observationally the efficiency of these mechanisms is not an easy task since many of them act at the same time, they do it in very different time scales, and in diverse regions of the cluster. However, there are some observational evidences that can be directly contrasted: i) morphological and structural distribution of the galaxies of the clusters; ii) luminosity function of galaxies in clusters; iii) diffuse light (quantity and distribution); iv) presence of galactic substructures within the clusters; v) spectro-photometric properties of dwarf and bright galaxies; vi) ICM properties. All these observables provide the necessary information to understand the relationship between environment and galactic evolution. These are the quantities this project aims at measuring for large samples of galaxy clusters.
Members
Results
- Intrinsic Shape of Galactic Bars. We find, for the first time, that 52% (16%) of bulges are thicker (flatter) than the surrounding bar. We suggest that these percentages might be representative of the fraction of classical and disc-like bulges in our sample, respectively.
- The Influence of the Environment in the Star Formation Quenching. Our results indicate that in low-density environments, post-starburst galaxies are formed by gas-rich minor mergers or accretions, whereas for high-density environments PSBs would be produced by the removal of the gas reservoirs of emission line galaxies by ram-pressure stripping.
- Morpho-Kinematic Properties of Galactic Bulges. We find that photometric diagnostics to separate different types of bulges (disc-like versus classical) might not be useful for S0 galaxies. Using the morpho-kinematics properties of S0 bulges derived in this paper we suggest that they are mainly formed by dissipational processes happening at high redshift.