General
The members of the Particle Astrophysics Group of the IAC participate actively in three large international collaborations of high-energy astrophysics: AMS-02 (Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer), the Cherenkov radiation telescopes MAGIC I and II and the Cherenkov Telescope Array Observatory (CTAO). We also participate in the ASTRI mini-array, the gamma-ray experiment Fermi-LAT and the gravitational wave follow-up optical telescopes GOTO.
AMS-02 is a particle detector designed to operate in space, onboard the International Space Station. It was successfully installed on the station on May 2011, and will operate during its lifetime till at least 2030. It is aimed at carrying out a high precision and high statistics study of the spectrum and composition of primary cosmic rays within a wide range of energies, as well as to look for primordial antimatter and dark matter in an indirect way.
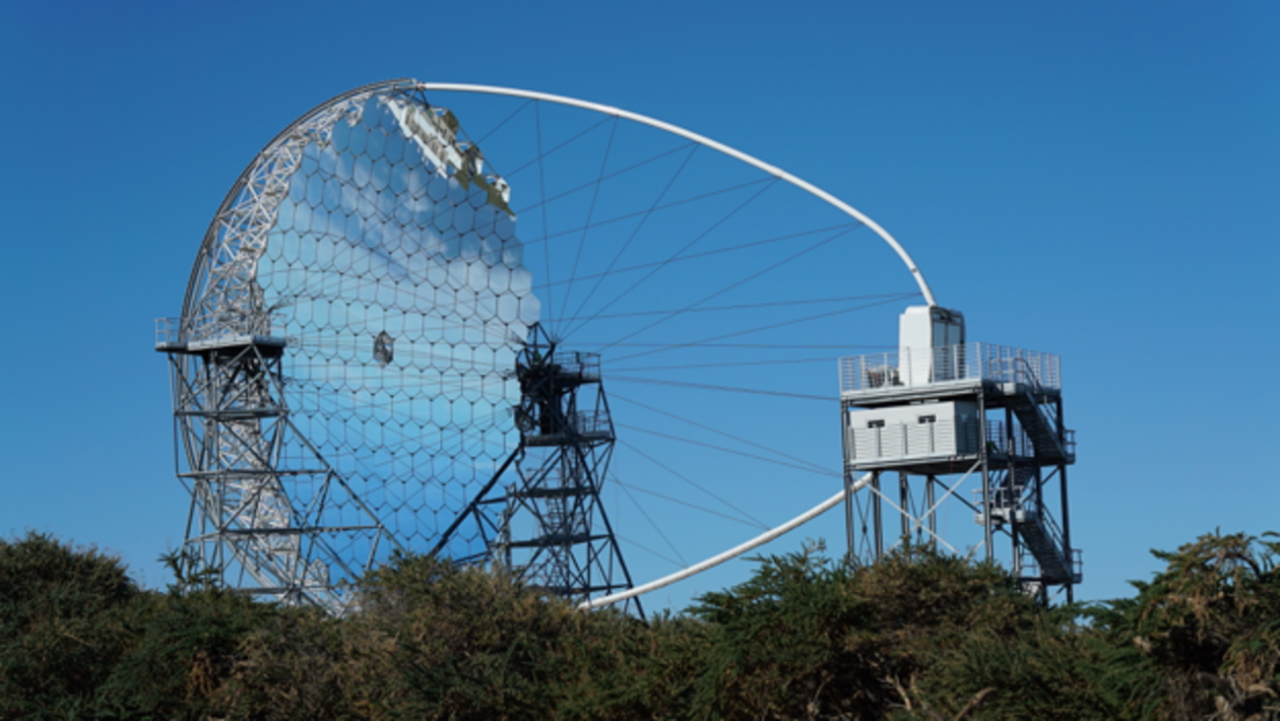
The MAGIC Collaboration is integrated by 20 research institutes and university departments from Armenia, Bulgaria, Finland, Germany, Italy, Poland, Spain, Switzerland and USA. The collaboration comprises two 17m diameter telescopes, located at the Roque de los Muchachos Observatory (ORM), designed to measure the Cherenkov radiation associated with atmospheric showers from very high-energy gamma rays.
In the context of gamma ray observations at very high energies, the IAC also participates in the international consortium of the array of Cherenkov telescopes CTAO, with the objective to build two large observatories in the Northern and Southern Hemispheres. The Roque de los Muchachos Observatory in La Palma was selected to host the CTA North observatory. The first telescope of 23 metres in diameter of the type "Large Size Telescope" of CTAO, know as LST1, was inaugurated in October 2018. This telescope was constructed by the "LST Collaboration" of CTAO, which consists of 300 scientists from 12 countries, where the IAC has a very relevant role. Currently the commissioning of the LST1 telescope is coming to and end and the scientific exploitation of the data is already given rise to new discoveries. The IAC is currently in the phase of constructing 3 more LST telescopes (LST2-LST4) in the ORM.
The ASTRI project is being currently built at the Teide Observatory. Its final design consist of 9 small size Cherenkov telescopes. The first telescope, ASTRI-1, is nowadays in commissioning phase.
Members
Results
Highlights of the project in 2025:
- Galactic transient sources with the Cherenkov Telescope Array Observatory (CTAO)
- Very high energy gamma ray observations of bright BL Lacs with the large size telescope LST1 of CTAO
- Development of a multi-wavelength workflow for different instruments that cover 11 orders of magnitude in energy
- Study of the gamma ray emission of SN 2024bch, a possible supernova of type IIn-L from a red supergiant progenitor
- Solar modulation of cosmic nuclei during a solar cycle with AMS-02
- Installation of the mechanical structures and mirrors of the telescopes LST2-LST4 of CTAO and the LST4 camera in the ORM. Installation of the mechanical structures of 7 telescopes of the ASTRI-miniarray and the ASTRI-3 camera in the OT. Quality control of the photomultipliers of the LST cameras
Scientific activity
Related publications
News