Bibcode
Mandolesi, N.; Maris, M.; Marleau, F.; Marshall, D. J.; Martínez-González, E.; Masi, S.; Matarrese, S.; Matthai, F.; Mazzotta, P.; Meinhold, P. R.; Melchiorri, A.; Melin, J.-B.; Mendes, L.; Mitra, S.; Miville-Deschênes, M.-A.; Montier, L.; Morgante, G.; Munshi, D.; Natoli, P.; Nørgaard-Nielsen, H. U.; Noviello, F.; Osborne, S.; Pajot, F.; Paoletti, D.; Partridge, B.; Pearson, T. J.; Perdereau, O.; Perrotta, F.; Piacentini, F.; Piat, M.; Pierpaoli, E.; Piffaretti, R.; Platania, P.; Pointecouteau, E.; Polenta, G.; Ponthieu, N.; Popa, L.; Poutanen, T.; Pratt, G. W.; Prunet, S.; Puget, J.-L.; Rachen, J. P.; Rebolo, R.; Reinecke, M.; Remazeilles, M.; Renault, C.; Ricciardi, S.; Ristorcelli, I.; Rocha, G.; Rosset, C.; Rossetti, M.; Rubiño-Martín, J. A.; Rusholme, B.; Sandri, M.; Savini, G.; Scott, D.; Starck, J.-L.; Stivoli, F.; Stolyarov, V.; Sudiwala, R.; Sunyaev, R.; Sutton, D.; Suur-Uski, A.-S.; Sygnet, J.-F.; Tauber, J. A.; Terenzi, L.; Toffolatti, L.; Tomasi, M.; Tristram, M.; Valenziano, L.; Van Tent, B.; Vielva, P.; Villa, F.; Vittorio, N.; Wandelt, B. D.; Weller, J.; White, S. D. M.; Yvon, D.; Zacchei, A.; Zonca, A.; Luzzi, G.; Macías-Pérez, J. F.; Maino, D.; Lilje, P. B.; Linden-Vørnle, M.; López-Caniego, M.; Le Jeune, M.; Leach, S.; Leonardi, R.; Liddle, A.; Lamarre, J.-M.; Lasenby, A.; Lawrence, C. R.; Lagache, G.; Knoche, J.; Kunz, M.; Kurki-Suonio, H.; Juvela, M.; Keihänen, E.; Khamitov, I. et al.
Bibliographical reference
Astronomy and Astrophysics, Volume 550, id.A129, 20 pp.
Advertised on:
2
2013
Journal
Citations
78
Refereed citations
76
Description
We examine the relation between the galaxy cluster mass M and
Sunyaev-Zeldovich (SZ) effect signal DA2
Y500 for a sample of 19 objects for which weak lensing (WL)
mass measurements obtained from Subaru Telescope data are available in
the literature. Hydrostatic X-ray masses are derived from XMM-Newton
archive data, and the SZ effect signal is measured from Planck all-sky
survey data. We find an MWL - DA2
Y500 relation that is consistent in slope and normalisation
with previous determinations using weak lensing masses; however, there
is a normalisation offset with respect to previous measures based on
hydrostatic X-ray mass-proxy relations. We verify that our SZ effect
measurements are in excellent agreement with previous determinations
from Planck data. For the present sample, the hydrostatic X-ray masses
at R500 are on average ~ 20 percent larger than the
corresponding weak lensing masses, which is contrary to expectations. We
show that the mass discrepancy is driven by a difference in mass
concentration as measured by the two methods and, for the present
sample, that the mass discrepancy and difference in mass concentration
are especially large for disturbed systems. The mass discrepancy is also
linked to the offset in centres used by the X-ray and weak lensing
analyses, which again is most important in disturbed systems. We outline
several approaches that are needed to help achieve convergence in
cluster mass measurement with X-ray and weak lensing observations.
Appendices are available in electronic form at http://www.aanda.org
Related projects
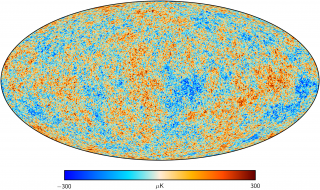
Anisotropy of the Cosmic Microwave Background
The general goal of this project is to determine and characterize the spatial and spectral variations in the temperature and polarisation of the Cosmic Microwave Background in angular scales from several arcminutes to several degrees. The primordial matter density fluctuations which originated the structure in the matter distribution of the present
Rafael
Rebolo López
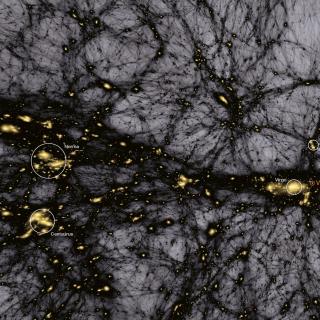
Cosmology with Large Scale Structure Probes
The Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB) contains the statistical information about the early seeds of the structure formation in our Universe. Its natural counterpart in the local universe is the distribution of galaxies that arises as a result of gravitational growth of those primordial and small density fluctuations. The characterization of the
FRANCISCO SHU
KITAURA JOYANES