Bibcode
Planck Collaboration; Ade, P. A. R.; Aghanim, N.; Alves, M. I. R.; Armitage-Caplan, C.; Arnaud, M.; Ashdown, M.; Atrio-Barandela, F.; Aumont, J.; Aussel, H.; Baccigalupi, C.; Banday, A. J.; Barreiro, R. B.; Barrena, R.; Bartelmann, M.; Bartlett, J. G.; Bartolo, N.; Basak, S.; Battaner, E.; Battye, R.; Benabed, K.; Benoît, A.; Benoit-Lévy, A.; Bernard, J.-P.; Bersanelli, M.; Bertincourt, B.; Bethermin, M.; Bielewicz, P.; Bikmaev, I.; Blanchard, A.; Bobin, J.; Bock, J. J.; Böhringer, H.; Bonaldi, A.; Bonavera, L.; Bond, J. R.; Borrill, J.; Bouchet, F. R.; Boulanger, F.; Bourdin, H.; Bowyer, J. W.; Bridges, M.; Brown, M. L.; Bucher, M.; Burenin, R.; Burigana, C.; Butler, R. C.; Calabrese, E.; Cappellini, B.; Cardoso, J.-F.; Carr, R.; Carvalho, P.; Casale, M.; Castex, G.; Catalano, A.; Challinor, A.; Chamballu, A.; Chary, R.-R.; Chen, X.; Chiang, H. C.; Chiang, L.-Y.; Chon, G.; Christensen, P. R.; Churazov, E.; Church, S.; Clemens, M.; Clements, D. L.; Colombi, S.; Colombo, L. P. L.; Combet, C.; Comis, B.; Couchot, F.; Coulais, A.; Crill, B. P.; Cruz, M.; Curto, A.; Cuttaia, F.; Da Silva, A.; Dahle, H.; Danese, L.; Davies, R. D.; Davis, R. J.; de Bernardis, P.; de Rosa, A.; de Zotti, G.; Déchelette, T.; Delabrouille, J.; Delouis, J.-M.; Démoclès, J.; Désert, F.-X.; Dick, J.; Dickinson, C.; Diego, J. M.; Dolag, K.; Dole, H.; Donzelli, S.; Doré, O.; Douspis, M.; Ducout, A.; Dunkley, J. et al.
Bibliographical reference
Astronomy and Astrophysics, Volume 571, id.A1, 48 pp.
Advertised on:
11
2014
Journal
Citations
1000
Refereed citations
958
Description
The European Space Agency’s Planck satellite, dedicated to
studying the early Universe and its subsequent evolution, was launched
14 May 2009 and has been scanning the microwave and submillimetre sky
continuously since 12 August 2009. In March 2013, ESA and the Planck
Collaboration released the initial cosmology products based on the first
15.5 months of Planck data, along with a set of scientific and technical
papers and a web-based explanatory supplement. This paper gives an
overview of the mission and its performance, the processing, analysis,
and characteristics of the data, the scientific results, and the science
data products and papers in the release. The science products include
maps of the cosmic microwave background (CMB) and diffuse extragalactic
foregrounds, a catalogue of compact Galactic and extragalactic sources,
and a list of sources detected through the Sunyaev-Zeldovich effect. The
likelihood code used to assess cosmological models against the Planck
data and a lensing likelihood are described. Scientific results include
robust support for the standard six-parameter ΛCDM model of
cosmology and improved measurements of its parameters, including a
highly significant deviation from scale invariance of the primordial
power spectrum. The Planck values for these parameters and others
derived from them are significantly different from those previously
determined. Several large-scale anomalies in the temperature
distribution of the CMB, first detected by WMAP, are confirmed with
higher confidence. Planck sets new limits on the number and mass of
neutrinos, and has measured gravitational lensing of CMB anisotropies at
greater than 25σ. Planck finds no evidence for non-Gaussianity in
the CMB. Planck’s results agree well with results from the
measurements of baryon acoustic oscillations. Planck finds a lower
Hubble constant than found in some more local measures. Some tension is
also present between the amplitude of matter fluctuations
(σ8) derived from CMB data and that derived from
Sunyaev-Zeldovich data. The Planck and WMAP power spectra are offset
from each other by an average level of about 2% around the first
acoustic peak. Analysis of Planck polarization data is not yet mature,
therefore polarization results are not released, although the robust
detection of E-mode polarization around CMB hot and cold spots is shown
graphically.
Related projects
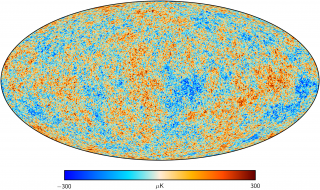
Anisotropy of the Cosmic Microwave Background
The general goal of this project is to determine and characterize the spatial and spectral variations in the temperature and polarisation of the Cosmic Microwave Background in angular scales from several arcminutes to several degrees. The primordial matter density fluctuations which originated the structure in the matter distribution of the present
Rafael
Rebolo López
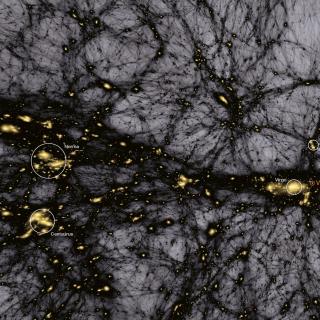
Cosmology with Large Scale Structure Probes
The Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB) contains the statistical information about the early seeds of the structure formation in our Universe. Its natural counterpart in the local universe is the distribution of galaxies that arises as a result of gravitational growth of those primordial and small density fluctuations. The characterization of the
FRANCISCO SHU
KITAURA JOYANES