General
MEDICAL TECHNOLOGY-IACTEC
IACTEC Medical Technology Program (TECMED) transfers technologies used in astrophysical research to the field of medicine, and is now developing two systems that operate in the visible, thermal infrared and microwave range of the electromagnetic spectrum. The researchers of the Medical Technology team belong to the IACTEC Training Program, supported by the Cabildo de Tenerife. Their results are been achieved thanks to the support of the Tenerife Island Council under the TFINNOVA 2016-2021 Training Program, the Strategic Framework for Insular Development (MEDI) and the Canary Islands Development Fund.
PINRELL
(Prototype for INfraREd analysis of Lower Limbs).
PINRELL is an Infrared Thermography system designed by the IACTEC Medical Technology program for the detection, analysis and evaluation of different pathologies, such as Diabetic Foot conditions. This prototype, developed especially for clinical use, is a tool designed for the early detection of possible subcutaneous lesions, infections and non-visible subcutaneous ulcers on the foot of diabetic patients, which are detectable in Thermal Infrared.
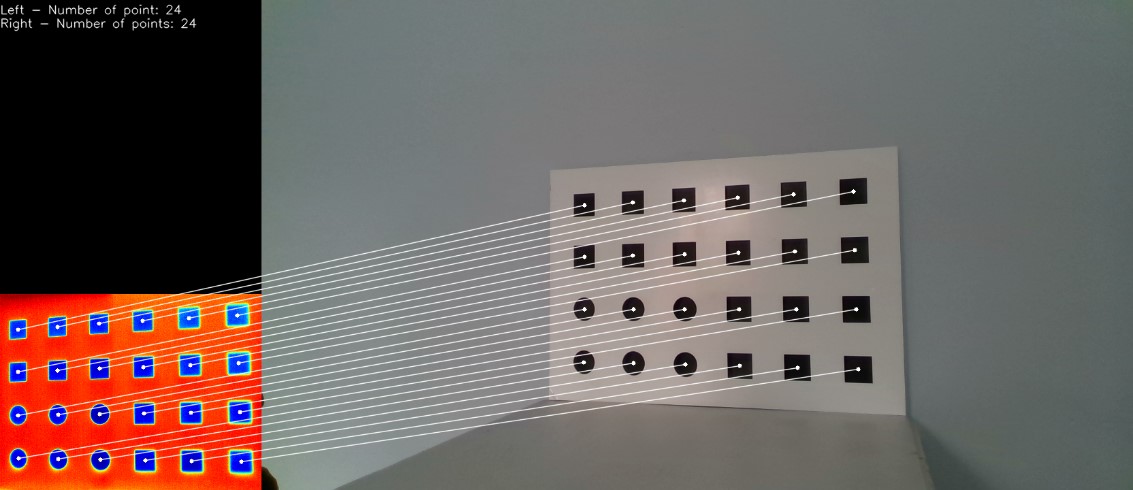

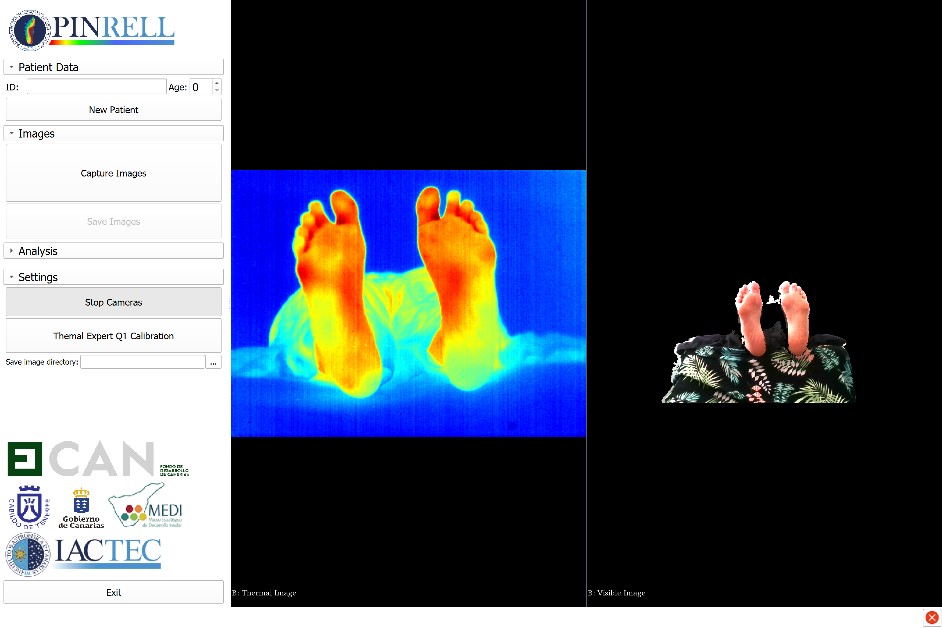

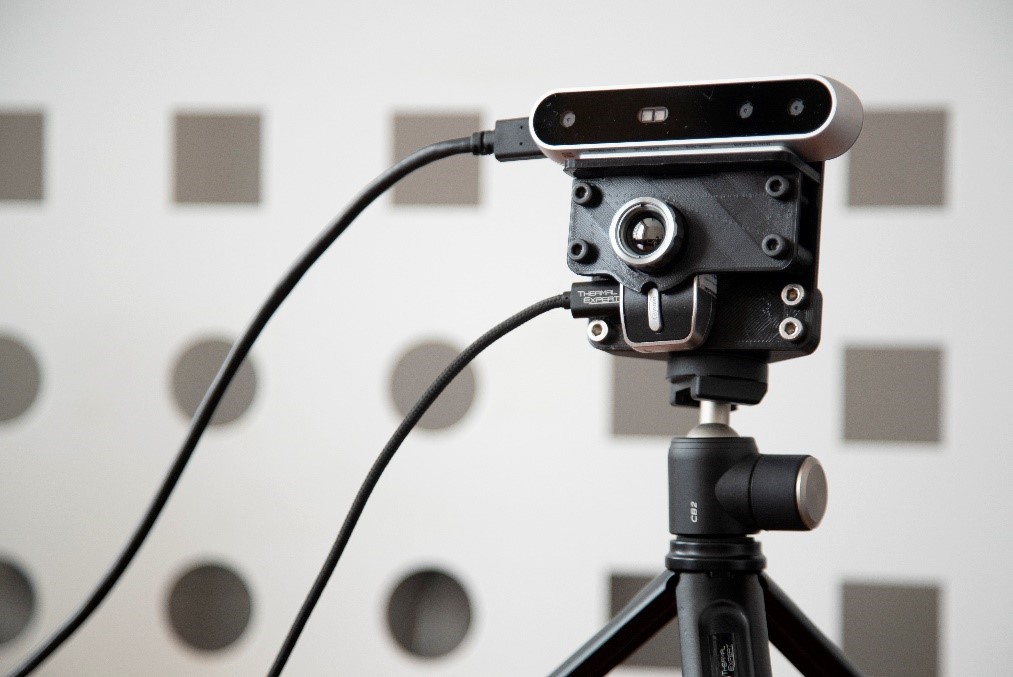
PINRELL uses three low-cost sensors for the detection of different ranges: Visible radiation (VIS) and Near Infrared (NIR) (from 0.4 µm to 0.86 µm) and Thermal Infrared (IR) (from 8 µm to 14 µm). In the VIS and NIR range, the prototype uses an Intel RealSense D415 camera. Its main characteristic is the generation of 3D depth information through two sensors and a NIR-type emitter, combining both in a sensor in the visible range (multi-channel image). Thermal IR range is covered by a Thermal Expert Q1 camera, which incorporates a micro-bolometer sensor with a QVGA resolution in the 8 µm - 14 µm range and a thermal sensitivity (NETD) of less than 50 mK.
One of the keys to the PINRELL prototype resides in the desktop software application developed by the TECMED program, which operates on two different operating systems: Linux and Windows. It has been developed using free software programs (3D Slicer and PLUS) and uses different standard software architectures applied in the software industry. The PINRELL software application is in charge of acquiring data, recording images and analyzing the information received by applying various data analysis techniques such as segmentation, classical statistical algorithms and Machine (Deep) Learning. In this way, the PINRELL system is capable of creating a multi-channel medical image database (VIS / IR / NIR) for the development of algorithms dedicated to the diagnosis and monitoring of diabetic foot neuropathies, performing an analysis and monitoring of abnormal patterns of surface temperature invisible to the human eye.

MICROWAVE
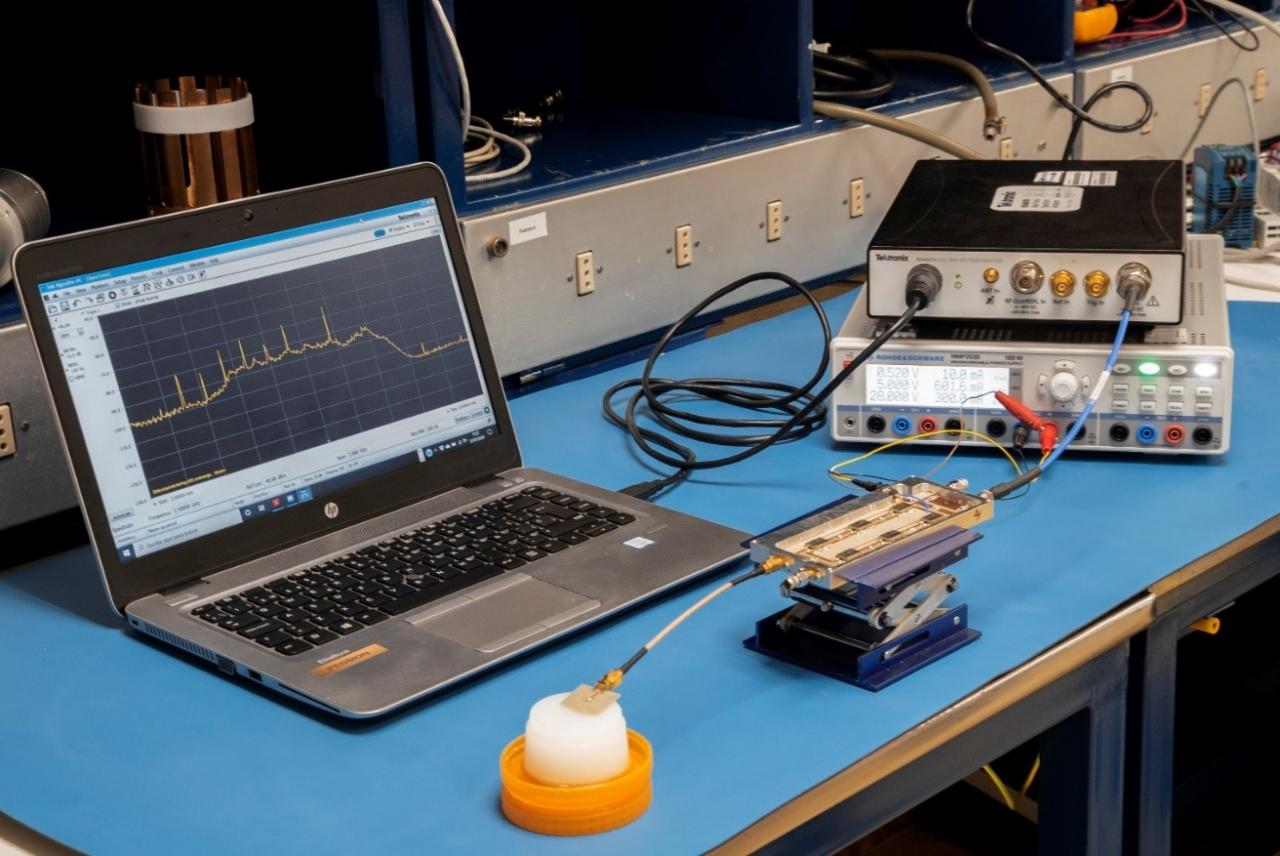
Microwave Radiometry (MWR) is a non-ionizing, non-invasive, passive and inherently safe technique to obtain internal body temperatures that provides subcutaneous in-depth temperature patterns. This technology will complement surface measurements of tissues aiming at a personalized medical diagnosis.
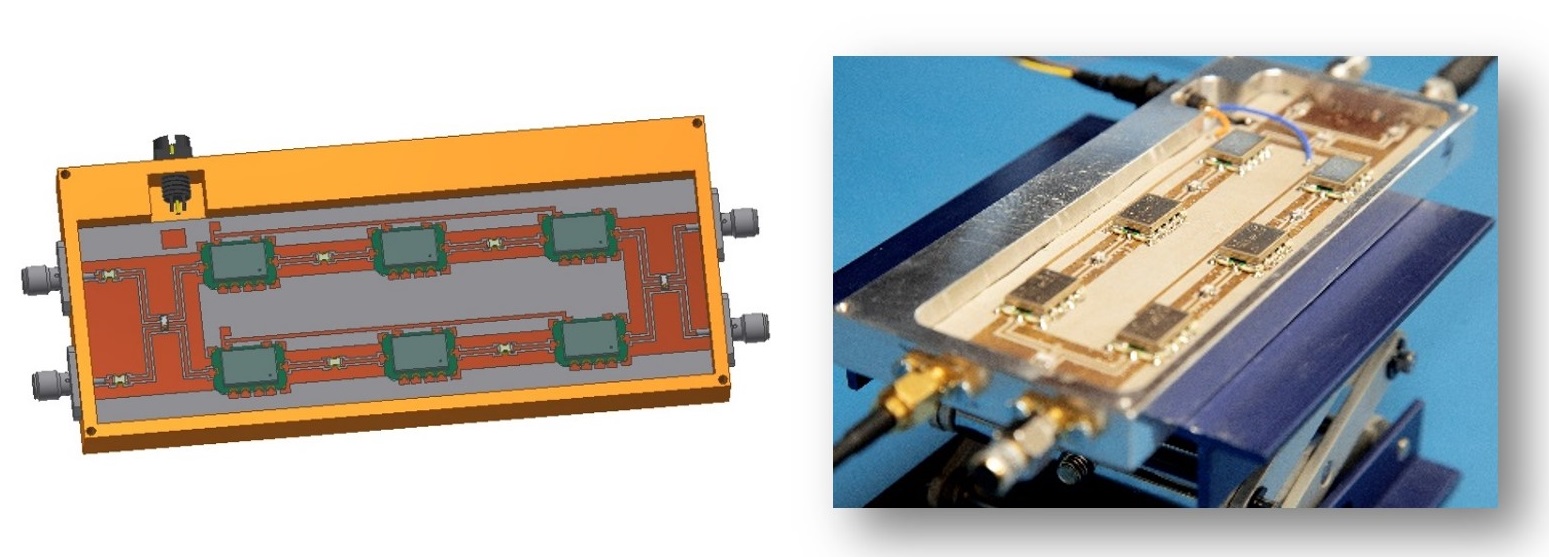
MWR is performed using radiometers, which are very sensitive low-noise receivers able to detect tiny incoming signals, such as the one radiated by human body tissues (around -174 dBm/Hz at 310 K – 37 ºC). The sensors developed at IACTEC operate at five bands (1.5 GHz, 2.2 GHz, 2.7 GHz, 3.5 GHz and 4.3 GHz) that are discriminated by using filters. These receivers have been thoroughly designed, confining and integrating over its operating bandwidth the incoming signal and adapting it to the detection window of the microwave sensors. The multi-frequency system will provide a set of temperature measurements that depends on each individual operation frequency leading to the analysis of the distribution of temperature inside biological tissues.
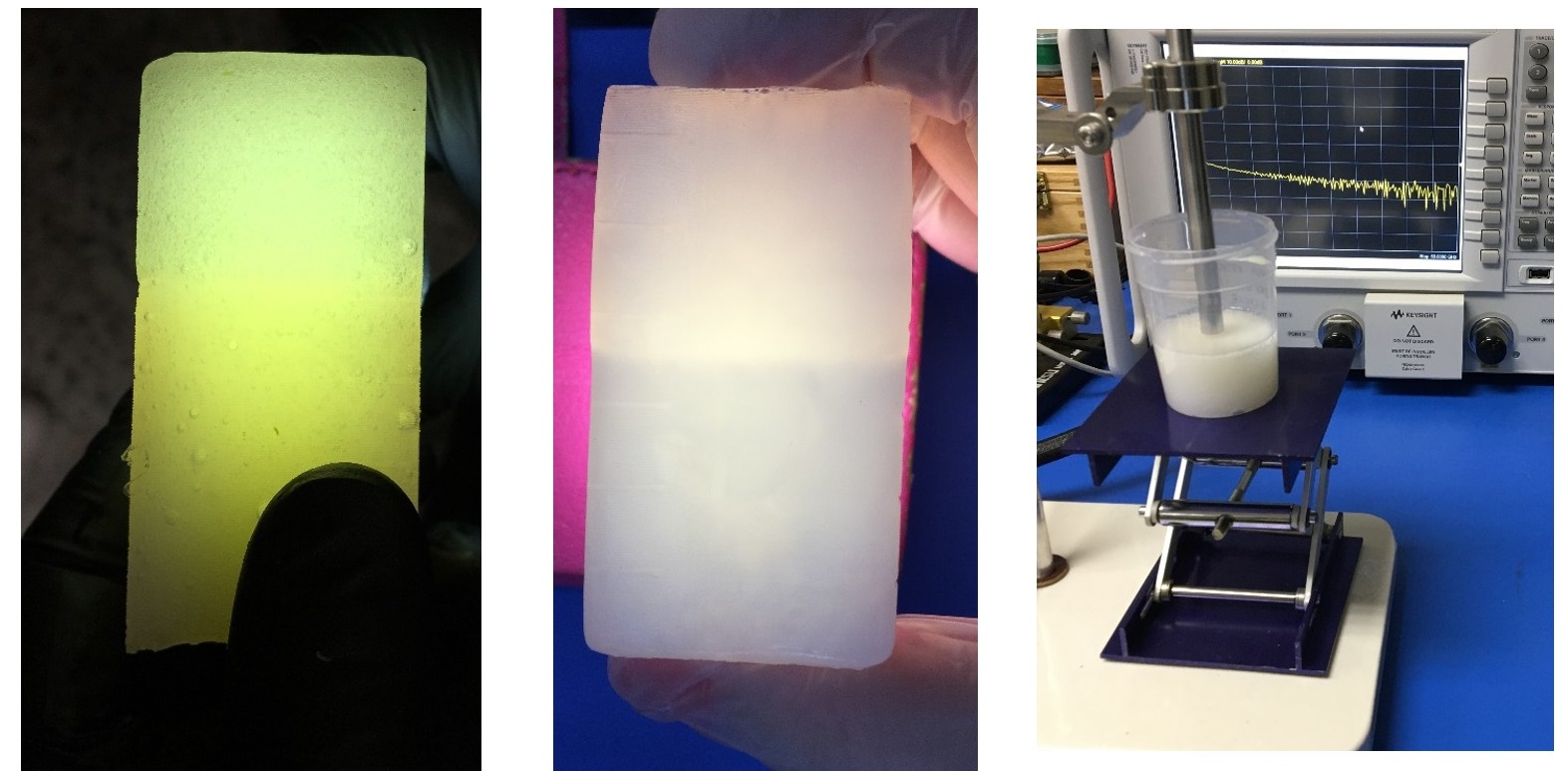
MWR also requires the development of components that realistically simulate the behaviour of the microwave energy inside biological tissues. These components are called phantoms, which accurately mimic the dielectric properties of body tissues. They are fabricated employing common materials with varying concentrations to provide the desired elasticity, consistency and longevity. A set of phantoms have been already made in multilayer and multimodality options, while anthropomorphic solutions are under development. They are all suitable for offer ultrasound (US) imaging modality, which enable the guidance of the microwave technology.
Members
Scientific activity
Related publications
Related conferences
-
Elaboración de fantomas para optimizar la utilidad Diagnóstico-Terapéutica de la Ecografía Torácica en la Práctica ClínicaCongreso SEPAR 2020Date-Past
-
Custom-made phantom designed for thoracic ultrasound diagnostic and therapeutic applications in clinical practiceEuropean Respiratory Society (ERS) International Congress (ERS 2020)Date-Past
-
Automatic Segmentation Based on Deep Learning Techniques for Diabetic Foot Monitoring Through Multimodal ImagesTemperature data acquired by infrared sensors provide relevant information to assess different medical pathologies in early stages, when the symptoms of the diseases are not visible yet to the naked20th International Conference on Image Analysis and Processing, Trento (Italy)Date-Past
-
Diseño de fantomas para optimizar la utilidad diagnóstico-terapéutica de la ecografía torácica en la práctica clínicaXXIV Congreso Regional NEUMOCANDate-Past







