Related grants:
General
This IAC research group carries out several extragalactic projects in different spectral ranges, using space as well as ground-based telescopes, to study the cosmological evolution of galaxies and the origin of nuclear activity in active galaxies. The group is a member of the international consortium which built the SPIRE instrument for the Herschel Space Observatory and of the European consortium which is developing the SAFARI instrument for the infrared space telescope SPICA of the space agencies ESA and JAXA.
The main projects in 2018 were:
a) High-redshift galaxies and quasars with far-infrared emission discovered with the Herschel Space Observatory in the HerMES and Herschel-ATLAS Key Projects.
b) Sloan Digital Sky Survey IV: BELLS GALLERY galaxies and very luminous Lyman alpha emitting galaxies.
c) Participation in the development of the SAFARI instrument, one of the European contributions to the SPICA infrared space telescope.
d) Discovery of the most distant individual star ever observed, in one of the fields of the "HST Frontier Fields".
e) Search for supernovae in distant, gravitationally lensed galaxies.
f) Several studies with GTC of absorption line systems in the line of sight to red quasars.
Members
Results
- Marques-Chaves et al. (2018) present a study of the submillimeter galaxy HLock01 at z = 2.9574, one of the brightest gravitationally lensed sources discovered in the Herschel Multi-tiered Extragalactic Survey. Detailed analysis of the high signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) rest-frame UV GTC OSIRIS spectrum shows complex kinematics of the gas.
- Rigopoulou et al. (2018) using new, Herschel spectroscopic observations of key far-infrared fine structure lines of the z ∼ 3 galaxy HLSW-01 derive gas-phase metallicities and find that the metallicities of z ∼ 3 submm-luminous galaxies are consistent with solar metallicities and that they appear to follow the mass–metallicity relation expected for z ∼ 3 systems.
- Cornachione et al. (2018) present a morphological study of 17 lensed Lyα emitter (LAE) galaxies of the BELLS GALLERY sample. The analysis combines the magnification effect of strong galaxy–galaxy lensing with the high resolution of the Hubble Space Telescope to achieve a physical resolution of ~80 pc for this 2 < z < 3 LAE sample.
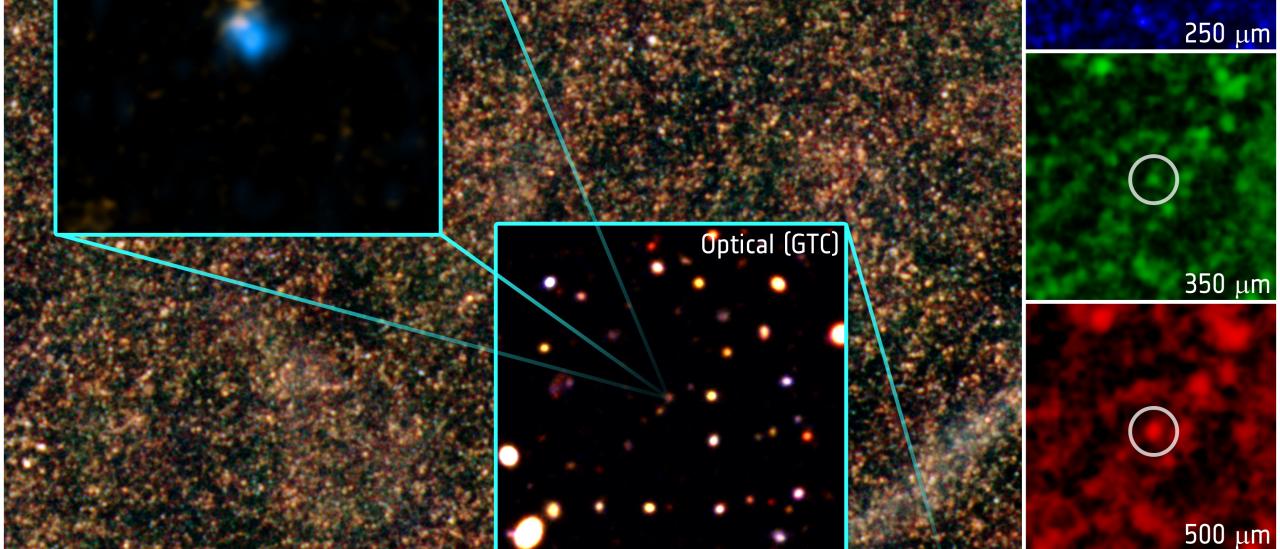
- Oteo et al. (2018) report the identification of an extreme protocluster of galaxies in the early universe whose core (nicknamed Distant Red Core, DRC, because of its very red color in Herschel SPIRE bands) is formed by at least 10 dusty star-forming galaxies (DSFGs), spectroscopically confirmed to lie at z = 4.002 via detection of emission lines with ALMA and ATCA.
- Kelly et al. (2018) report the discovery of an individual star, Icarus, at redshift z = 1.49 magnified by more than × 2,000 by gravitational lensing of the galaxy cluster MACS J1149+222. Icarus is located in a spiral galaxy that is so far from Earth that its light has taken 9000 million years to reach the Earth.