Related grants:
General
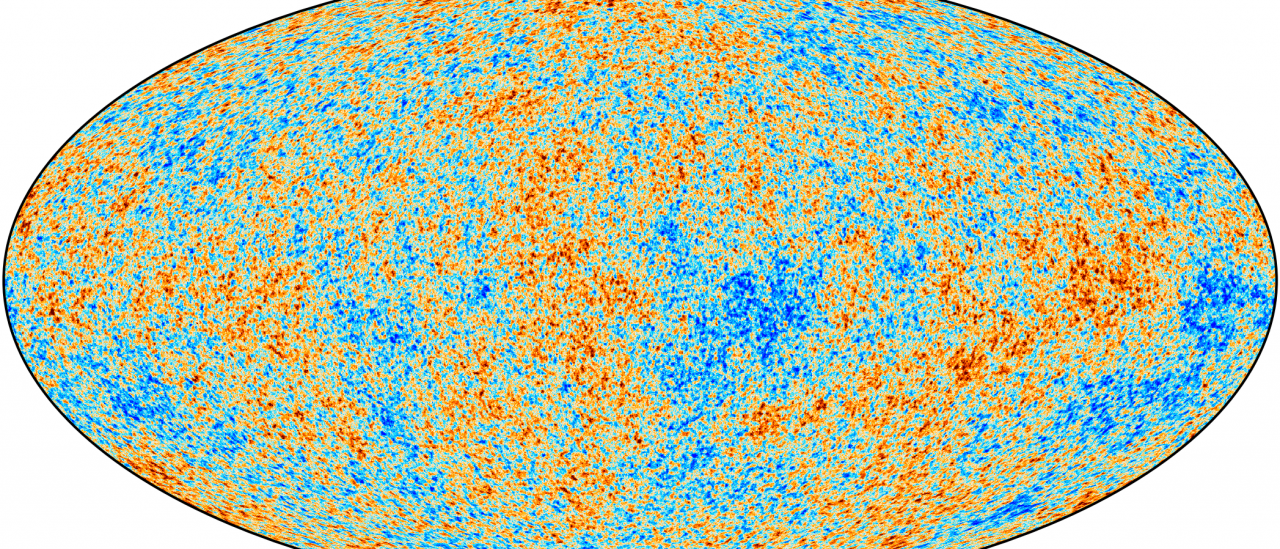
The general goal of this project is to determine and characterize the spatial and spectral variations in the temperature and polarisation of the Cosmic Microwave Background in angular scales from several arcminutes to several degrees. The primordial matter density fluctuations which originated the structure in the matter distribution of the present Universe, left imprinted inhomogeneities in the CMB temperature distribution, that are mathematically encoded in the so-called angular power spectrum. Initially, pioneering experiments like the COBE satellite (whose results deserved the Nobel Prize on Physics 2006) or the Tenerife CMB experiment demonstrated in the 90s that the level of anisotropy was about one part in a hundred thousands at angular scales of several degrees. Obtaining CMB maps at various frequencies with sufficient sensitivity to detect structures at this level is of fundamental importance to extract information on the power spectrum of primordial density fluctuations, to prove the existence of an inflationary period in the Early Universe and to establish the ultimate nature of the dark matter and dark energy. Recently, the WMAP satellite obtained CMB maps with unprecedented sensitivity that allowed to set restrictions on a large number of cosmological parameters.
The focus of this project is to undertake measurements at gradually higher angular resolutions and sensitivities, by using different experiments that have been operative from the Teide Observatory, like the Tenerife experiment, the IAC-Bartol experiment or the JBO-IAC interferometer. More recently, the Very Small Array interferometer performed observations between 1999 and 2008. At that time the COSMOSOMAS experiment was also operative, its goal having been not only the characterization of the primary CMB anisotropies but also the study and characterization of the Galactic foreground contamination. In more recent years the activity in this project has focused in the scientific exploitation of data from the Planck satellite, and in the development, operation and exploitation of the QUIJOTE experiment. Now that the Planck mission has been completed and finished, the activity is focused in the scientific exploitation of QUIJOTE, in the development of new instrumentation for QUIJOTE, and in in the development of new experiments that are being deployed or that will be deployed at the Teide Observatory: GroundBRID, STRIP, KISS and TMS.
Members
Results
- 6-7 june: XV QUIJOTE Scientific Meeting (IFCA, Santander)
- July: publication of the final results (12 articles) and data from the Planck satellite.
- 15-19 october: "CMB foregrounds for B-mode studies" conference, organised within the Radioforegrounds proyect, IV AME workshop, and XVI QUIJOTE Scientific Meeting (all these eventes were celebrated at the IAC)
- October: installation of the dome of the GroundBIRD experiment, at the Teide Observatory.
- December: aceptation of the third QUIJOTE scientific article (Poidevin et al. 2019)
Scientific activity
Related conferences
-
XIX Canary Islands Winter School of Astrophysics "The Cosmic Microwave | Background: from quantum fluctuations to the present Universe"Tenerife, Canary IslandsSpainDate-Past