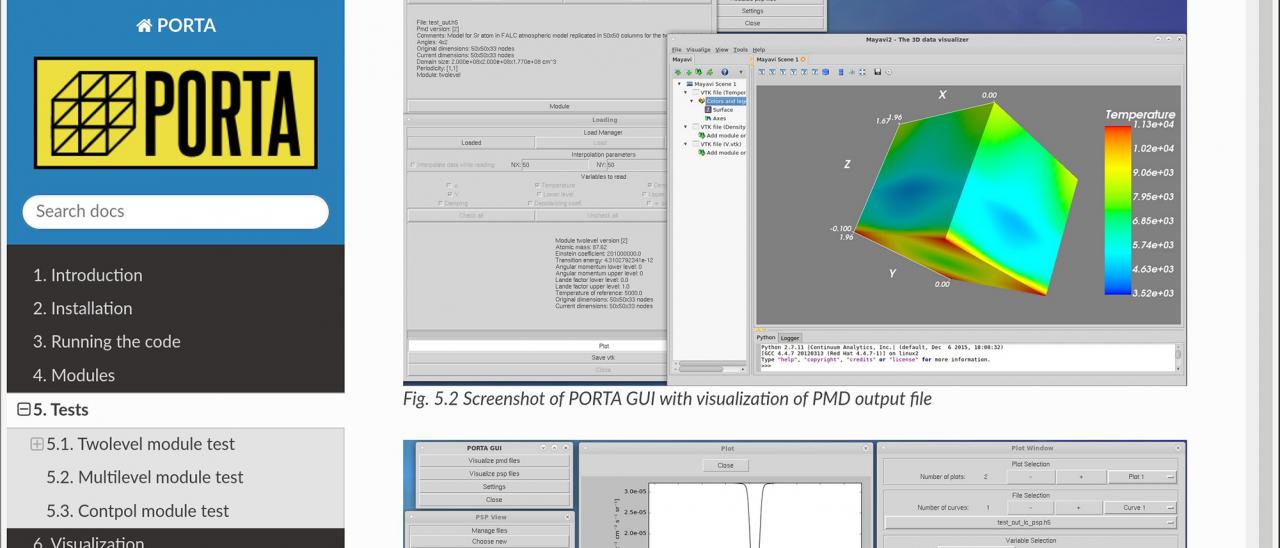
The POLMAG research team of the Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias (IAC), which includes scientists from other international institutions, has released the public version of PORTA, an advanced radiative transfer code to solve the problem of the generation and transfer of polarized radiation in realistic three-dimensional (3D) models of stellar atmospheres. PORTA allows scientists to plan and model spectropolarimetric observations with today’s telescopes.
This public version of PORTA offered to the astrophysical community comes with several modules useful for considering several problems of interest for the planning and interpretation of spectropolarimetric observations with the new generation of solar telescopes, such as the present Daniel K. Inouye Solar Telescope (Hawaii, USA) and the future European Solar Telescope (Canary Islands, Spain). The code can be applied to solve the non-equilibrium problem of polarized radiation in 3D models of stellar atmospheres, including that of the Sun. PORTA takes fully into account the symmetry breaking effects produced by the model’s horizontal inhomogeneities and macroscopic velocity gradients, a fundamental physical ingredient to correctly synthesize the polarization of the electromagnetic radiation produced in stars.
PORTA can be applied to model the intensity and polarization of spectral lines (i.e., the four Stokes parameters) within the framework of the quantum theory of light polarization (see Stepan & Trujillo Bueno 2013; Astronomy & Astrophysics, 557, 143). With the public version the user can perform a variety of radiative transfer numerical experiments, taking into account either the combined action of anisotropic radiation pumping and the Hanle and Zeeman effects, only scattering processes and the Hanle effect, or just the impact of the Zeeman effect, on the polarization of the emergent spectral line radiation. The parallelization strategy of PORTA facilitates the numerical solution of complex 3D radiative transfer problems using massively parallel supercomputers, such as the MareNostrum computer of the Barcelona Supercomputing Center.
The public version of PORTA is one of the objectives of the POLMAG research group, which is funded by the Advanced Grant awarded by the European Research Council (ERC) to Javier Trujillo Bueno (CSIC Research Professor and IAC Senior Scientist). The other members of the group thanks to which the public version of PORTA is now a reality are Tanausú del Pino Alemán (IAC), Ángel de Vicente Garrido (IAC), Jaume Jaume Bestard (IAC), and Jiri Stepan (Astronomical Institute of the Czech Academy of Sciences).
PORTA is under continuous development and new features and modules will be implemented. The latest version of PORTA can be found in the “Codes” section of the webpage of the POLMAG group (see http://research.iac.es/proyecto/polmag/).
PORTA is offered to the astrophysical community with the hope that it will be applied for achieving new advances in solar and stellar physics.
Link to the POLMAG project video: https://youtu.be/mwJxddrDzkk