Bibcode
Davies, J. I.; Wilson, C. D.; Auld, R.; Baes, M.; Barlow, M. J.; Bendo, G. J.; Bock, J. J.; Boselli, A.; Bradford, M.; Buat, V.; Castro-Rodriguez, N.; Chanial, P.; Charlot, S.; Ciesla, L.; Clements, D. L.; Cooray, A.; Cormier, D.; Cortese, L.; Dwek, E.; Eales, S. A.; Elbaz, D.; Galametz, M.; Galliano, F.; Gear, W. K.; Glenn, J.; Gomez, H. L.; Griffin, M.; Hony, S.; Isaak, K. G.; Levenson, L. R.; Lu, N.; Madden, S.; O'Halloran, B.; Okumura, K.; Oliver, S.; Page, M. J.; Panuzzo, P.; Papageorgiou, A.; Parkin, T. J.; Perez-Fournon, I.; Pohlen, M.; Rangwala, N.; Rigby, E. E.; Roussel, H.; Rykala, A.; Sacchi, N.; Sauvage, M.; Schulz, B.; Schirm, M. R. P.; Smith, M. W. L.; Spinoglio, L.; Stevens, J. A.; Srinivasan, S.; Symeonidis, M.; Trichas, M.; Vaccari, M.; Vigroux, L.; Wozniak, H.; Wright, G. S.; Zeilinger, W. W.
Bibliographical reference
Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, Volume 409, Issue 1, pp. 102-108.
Advertised on:
11
2010
Citations
24
Refereed citations
23
Description
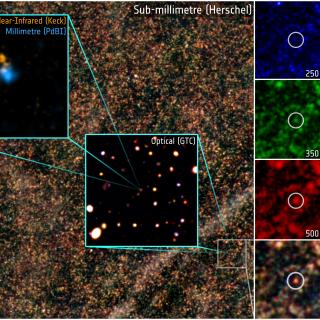
Galactic cirrus emission at far-infrared wavelengths affects many
extragalactic observations. Separating this emission from that
associated with extragalactic objects is both important and difficult.
In this paper we discuss a particular case, the M81 group, and the
identification of diffuse structures prominent in the infrared, but also
detected at optical wavelengths. The origin of these structures has
previously been controversial, ranging from them being the result of a
past interaction between M81 and M82 or due to more local Galactic
emission. We show that over an order of a few arcmin scales, the
far-infrared (Herschel 250μm) emission correlates spatially very well
with a particular narrow-velocity (2-3 kms-1) component of
the Galactic HI. We find no evidence that any of the far-infrared
emission associated with these features actually originates in the M81
group. Thus we infer that the associated diffuse optical emission must
be due to galactic light-back scattered off dust in our galaxy.
Ultraviolet observations pick out young stellar associations around M81,
but no detectable far-infrared emission. We consider in detail one of
the Galactic cirrus features, finding that the far-infrared HI relation
breaks down below arcmin scales and that at smaller scales there can be
quite large dust-temperature variations.
Related projects
Formation and Evolution of Galaxies: Observations in Infrared and other Wavelengths
This IAC research group carries out several extragalactic projects in different spectral ranges, using space as well as ground-based telescopes, to study the cosmological evolution of galaxies and the origin of nuclear activity in active galaxies. The group is a member of the international consortium which built the SPIRE instrument for the
Ismael
Pérez Fournon