Bibcode
Cava, A.; Rodighiero, G.; Pérez-Fournon, I.; Buitrago, F.; Trujillo, I.; Altieri, B.; Amblard, A.; Auld, R.; Bock, J.; Brisbin, D.; Burgarella, D.; Castro-Rodríguez, N.; Chanial, P.; Cirasuolo, M.; Clements, D. L.; Conselice, C. J.; Cooray, A.; Eales, S.; Elbaz, D.; Ferrero, P.; Franceschini, A.; Glenn, J.; Solares, E. A. González; Griffin, M.; Ibar, E.; Ivison, R. J.; Marchetti, L.; Morrison, G. E.; Mortier, A. M. J.; Oliver, S. J.; Page, M. J.; Papageorgiou, A.; Pearson, C. P.; Pohlen, M.; Rawlings, J. I.; Raymond, G.; Rigopoulou, D.; Roseboom, I. G.; Rowan-Robinson, M.; Scott, D.; Seymour, N.; Smith, A. J.; Symeonidis, M.; Tugwell, K. E.; Vaccari, M.; Valtchanov, I.; Vieira, J. D.; Vigroux, L.; Wang, L.; Wright, G.
Bibliographical reference
Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society: Letters, Volume 409, Issue 1, pp. L19-L24.
Advertised on:
11
2010
Citations
15
Refereed citations
14
Description
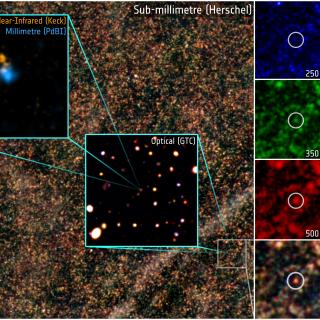
We have analysed the rest-frame far-infrared properties of a sample of
massive (M* > 1011Msolar) galaxies
at 2 <~ z <~ 3 in the Great Observatories Origins Deep
Survey-North (GOODS-N) field using the Spectral and Photometric Imaging
Receiver (SPIRE) instrument aboard the Herschel Space Observatory. To
conduct this analysis we take advantage of the data from the Herschel
Multi-tiered Extragalactic Survey (HerMES) key programme. The sample
comprises 45 massive galaxies with structural parameters characterized
with HST NICMOS-3. We study detections at submm Herschel bands, together
with Spitzer 24-μm data, as a function of the morphological type,
mass and size. We find that 26/45 sources are detected at MIPS 24 μm
and 15/45 (all MIPS 24-μm detections) are detected at SPIRE 250
μm, with disc-like galaxies more easily detected. We derive star
formation rates (SFRs) and specific star formation rates (sSFRs) by
fitting the spectral energy distribution of our sources, taking into
account non-detections for SPIRE and systematic effects for MIPS derived
quantities. We find that the mean SFR for the spheroidal galaxies
(~50-100Msolaryr-1) is substantially (a factor ~3)
lower than the mean value presented by disc-like galaxies
(~250-300Msolaryr-1).
Related projects
Formation and Evolution of Galaxies: Observations in Infrared and other Wavelengths
This IAC research group carries out several extragalactic projects in different spectral ranges, using space as well as ground-based telescopes, to study the cosmological evolution of galaxies and the origin of nuclear activity in active galaxies. The group is a member of the international consortium which built the SPIRE instrument for the
Ismael
Pérez Fournon

Traces of Galaxy Formation: Stellar populations, Dynamics and Morphology
We are a large, diverse, and very active research group aiming to provide a comprehensive picture for the formation of galaxies in the Universe. Rooted in detailed stellar population analysis, we are constantly exploring and developing new tools and ideas to understand how galaxies came to be what we now observe.
Anna
Ferré Mateu