Bibcode
Smith, A. J.; Wang, L.; Oliver, S. J.; Auld, R.; Bock, J.; Brisbin, D.; Burgarella, D.; Chanial, P.; Chapin, E.; Clements, D. L.; Conversi, L.; Cooray, A.; Dowell, C. D.; Eales, S.; Farrah, D.; Franceschini, A.; Glenn, J.; Griffin, M.; Ivison, R. J.; Mortier, A. M. J.; Page, M. J.; Papageorgiou, A.; Pearson, C. P.; Pérez-Fournon, I.; Pohlen, M.; Rawlings, J. I.; Raymond, G.; Rodighiero, G.; Roseboom, I. G.; Rowan-Robinson, M.; Savage, R.; Scott, Douglas; Seymour, N.; Symeonidis, M.; Tugwell, K. E.; Vaccari, M.; Valtchanov, I.; Vigroux, L.; Ward, R.; Wright, G.; Zemcov, M.
Bibliographical reference
Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, Volume 419, Issue 1, pp. 377-389.
Advertised on:
1
2012
Citations
67
Refereed citations
66
Description
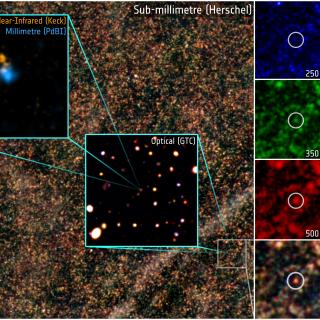
We describe the generation of single-band point source catalogues from
submillimetre Herschel-SPIRE observations taken as part of the Science
Demonstration Phase of the Herschel Multi-tiered Extragalactic Survey
(HerMES). Flux densities are found by means of peak finding and the
fitting of a Gaussian point-response function. With highly confused
images, careful checks must be made on the completeness and flux-density
accuracy of the detected sources. This is done by injecting artificial
sources into the images and analysing the resulting catalogues. Measured
flux densities at which 50 per cent of injected sources result in good
detections at (250, 350 and 500) μm range from (11.6, 13.2 and 13.1)
to (25.7, 27.1 and 35.8) mJy, depending on the depth of the observation
(where a 'good' detection is taken to be one with positional offset less
than one full-width half-maximum of the point-response function, and
with the measured flux density within a factor of 2 of the flux density
of the injected source). This paper acts as a reference for the 2010
July HerMES public data release. Herschel is an ESA space observatory
with science instruments provided by European-led Principal Investigator
consortia and with important participation from NASA.
Related projects
Formation and Evolution of Galaxies: Observations in Infrared and other Wavelengths
This IAC research group carries out several extragalactic projects in different spectral ranges, using space as well as ground-based telescopes, to study the cosmological evolution of galaxies and the origin of nuclear activity in active galaxies. The group is a member of the international consortium which built the SPIRE instrument for the
Ismael
Pérez Fournon

Formation and Evolution of Galaxies: Observations in Infrared and other Wavelengths
This IAC research group carries out several extragalactic projects in different spectral ranges, using space as well as ground-based telescopes, to study the cosmological evolution of galaxies and the origin of nuclear activity in active galaxies. The group is a member of the international consortium which built the SPIRE instrument for the
Ismael
Pérez Fournon