Bibcode
Petitpas, G.; Pearson, C. P.; Papageorgiou, A.; Page, M. J.; Omont, A.; Oliver, S. J.; O'Halloran, B.; Nguyen, H. T.; Morrison, G. E.; Marsden, G.; Martínez-Navajas, P.; Marchetti, L.; Laporte, N.; Ivison, R. J.; Ibar, E.; Heinis, S.; Hatziminaoglou, E.; Halpern, M.; Gurwell, M. A.; Griffin, M.; Franceschini, A.; Farrah, D.; Ellsworth-Bowers, T. P.; De Bernardis, F.; Dannerbauer, H.; Cooray, A.; Conversi, L.; Clements, D. L.; Chapman, S. C.; Casey, C. M.; Cabrera-Lavers, A.; Burgarella, D.; Buat, V.; Bridge, C.; Boselli, A.; Bock, J.; Béthermin, M.; Bertoldi, F.; Aussel, H.; Asboth, V.; Arumugam, V.; Glenn, J.; Conley, A.; Dowell, C. D.; Zemcov, M.; Xu, C. K.; Wardlow, J.; Wang, L.; Viero, M.; Vieira, J. D.; Valtchanov, I.; Vaccari, M.; Symeonidis, M.; Streblyanska, A.; Smith, A. J.; Shupe, D. L.; Seymour, N.; Scott, Douglas; Schulz, B.; Sayers, J.; Rowan-Robinson, M.; Roseboom, I. G.; Rigopoulou, D.; Riechers, D.; Pohlen, M.; Pérez-Fournon, I.
Bibliographical reference
The Astrophysical Journal, Volume 780, Issue 1, article id. 75, 24 pp. (2014).
Advertised on:
1
2014
Journal
Citations
106
Refereed citations
98
Description
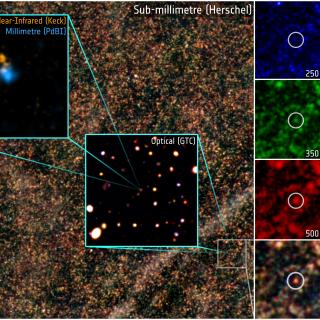
We present a method for selecting z > 4 dusty, star-forming galaxies
(DSFGs) using Herschel/Spectral and Photometric Imaging Receiver
250/350/500 μm flux densities to search for red sources. We apply
this method to 21 deg2 of data from the HerMES survey to
produce a catalog of 38 high-z candidates. Follow-up of the first five
of these sources confirms that this method is efficient at selecting
high-z DSFGs, with 4/5 at z = 4.3-6.3 (and the remaining source at z =
3.4), and that they are some of the most luminous dusty sources known.
Comparison with previous DSFG samples, mostly selected at longer
wavelengths (e.g., 850 μm) and in single-band surveys, shows that our
method is much more efficient at selecting high-z DSFGs, in the sense
that a much larger fraction are at z > 3. Correcting for the
selection completeness and purity, we find that the number of bright (S
500 μm >= 30 mJy), red Herschel sources is 3.3 ±
0.8 deg–2. This is much higher than the number
predicted by current models, suggesting that the DSFG population extends
to higher redshifts than previously believed. If the shape of the
luminosity function for high-z DSFGs is similar to that at z ~ 2,
rest-frame UV based studies may be missing a significant component of
the star formation density at z = 4-6, even after correction for
extinction.
.
Herschel is an ESA space observatory with science instruments provided
by European-led Principal Investigator consortia and with important
participation from NASA.
Related projects
Formation and Evolution of Galaxies: Observations in Infrared and other Wavelengths
This IAC research group carries out several extragalactic projects in different spectral ranges, using space as well as ground-based telescopes, to study the cosmological evolution of galaxies and the origin of nuclear activity in active galaxies. The group is a member of the international consortium which built the SPIRE instrument for the
Ismael
Pérez Fournon