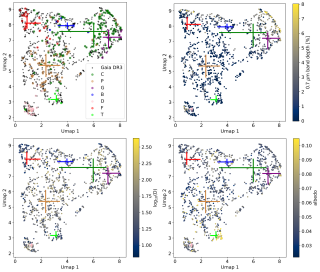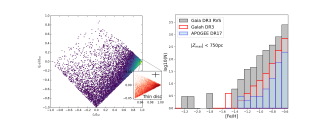
The formation and evolution of the disk of our Galaxy, the Milky Way, remains an enigma in astronomy. In particular, the relationship between the thick disk and the thin disk —two key components of the Milky Way— is still unclear. Understanding the chemical and dynamical properties of the stars within these disks is crucial, especially in the parameter spaces where their characteristics overlap, such the metallicity regime around [Fe/H] ~ -0.7, which marks the metal-poor end of the thin disk, higher than that of the thick disk. This is often interpreted as an indication that the thin disk
Advertised on