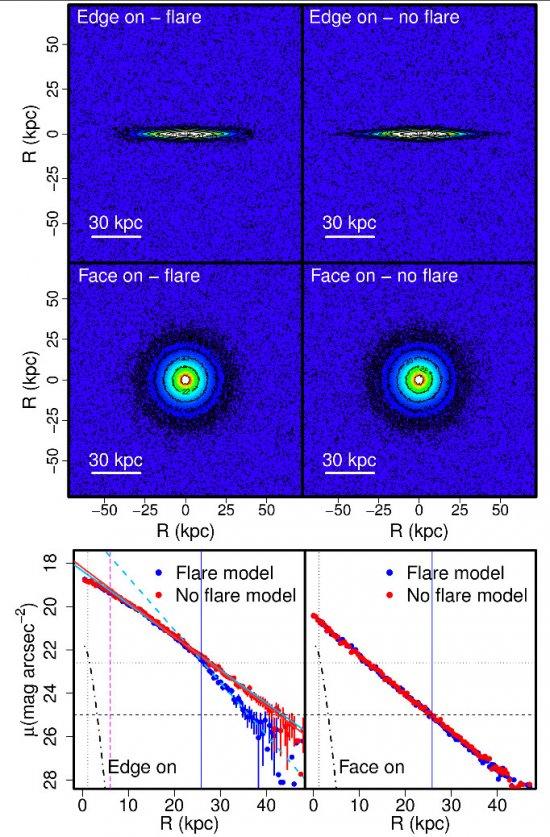
Previous numerical studies had apparently ruled out the possibility that flares in galaxy discs could give rise to the apparent breaks in their luminosity profiles when observed edge-on. However the studies have not, until now, analysed this hypothesis systematically using realistic models for the disc, the flare, and the bulge. We revisit this theme by analysing a series of models which sample a wide range of observationally based structural parameters for these three components. Using observational data, we have considered realistic distributions of bulge-to-disc ratios, morphological parameters of bulges and discs, vertical scale heights of discs and their radial gradients defining the flare for different morphological types and stellar mass bins. The surface brightness profiles for the face-on and edge-on views of each model were simulated to find out whether the flared disc produces a Type-II break in the disc profile when observed edge-on, and if so under what conditions. Contrary to previous claims, we find that discs with realistic flares can produce significant breaks in discs when observed edge-on. Specifically a flare with the parameters of that of the Milky Way would produce a significant break of the disc at a RbrkII of ~8.6 kpc if observed edge-on. Central bulges have no significant effects on the results. These simulations show that flared discs can explain the existence of many Type-II breaks observed in edge-on galaxies, in a range of galaxies with intermediate to low break strength values of -0.25 <S< -0.1.
Edge-on I-band images for the flared and non-flared models. Intermediate panels: The same for the face-on discs. Bottom panels: Surface brightness profiles in the major axis of the galaxy for edge-on (left) and the face-on (right) views of the two models
Advertised on
References