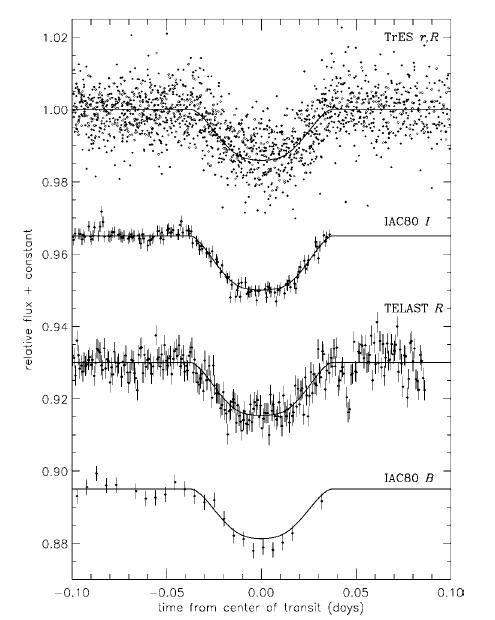
In August 2006 a new planetary transit was discovered from data from the TrES network. The discovery was confirmed using radial velocity curves obtained with the Keck and characterised with light curves in different filters obtained using two telescopes at the Observatorio del Teide: "IAC80" and "TELAST" (the first result of scientific interest obtained from the latter). The planet discovered, TrES-2, is more massive and somewhat larger than its quasi-homonym TrES-1 (the first exoplanet discovered using the transit method), and follows the expected patterns for this type of object. Its main importance is that it is the first object discovered in the area of observation of the future Kepler satellite, which will be able to track it in a degree of detail never before achieved.
Light curves of TRES_2 obtained using telescopes of the network and with two telescopes from the Observatorio del Teide: "IAC-80" and "TELAST" with different filters.
Advertised on
It may interest you
-
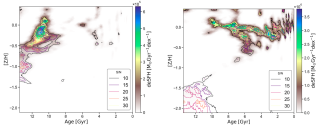 Research on the formation, origin, and evolution of the dichotomy between the thin and thick disk components of the Milky Way has been a major topic of study, as it is key to understanding how our Galaxy formed. However, this is not an easy task, since populations defined by their morphology or kinematics show a mixture of chemically distinct stellar populations. Age therefore becomes a fundamental parameter for understanding the evolution of the Galactic disk. Our goal is to derive the age and metallicity distributions of the thin and thick disks defined kinematically, in order to revealAdvertised on
Research on the formation, origin, and evolution of the dichotomy between the thin and thick disk components of the Milky Way has been a major topic of study, as it is key to understanding how our Galaxy formed. However, this is not an easy task, since populations defined by their morphology or kinematics show a mixture of chemically distinct stellar populations. Age therefore becomes a fundamental parameter for understanding the evolution of the Galactic disk. Our goal is to derive the age and metallicity distributions of the thin and thick disks defined kinematically, in order to revealAdvertised on -
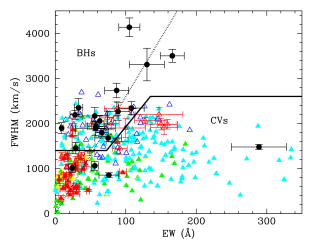 Dormant black holes in X-ray transients can be identified by the presence of broad Hα emission lines from quiescent accretion discs. Unfortunately, short-period cataclysmic variables can also produce broad Hα lines, especially when viewed at high inclinations, and are thus a major source of contamination. Here we compare the full width at half maximum (FWHM) and equivalent width (EW) of the Hα line in a sample of 20 quiescent black hole transients and 354 cataclysmic variables (305 from SDSS I to IV) with secure orbital periods (Porb) and find that: (1) FWHM and EW values decrease with PorbAdvertised on
Dormant black holes in X-ray transients can be identified by the presence of broad Hα emission lines from quiescent accretion discs. Unfortunately, short-period cataclysmic variables can also produce broad Hα lines, especially when viewed at high inclinations, and are thus a major source of contamination. Here we compare the full width at half maximum (FWHM) and equivalent width (EW) of the Hα line in a sample of 20 quiescent black hole transients and 354 cataclysmic variables (305 from SDSS I to IV) with secure orbital periods (Porb) and find that: (1) FWHM and EW values decrease with PorbAdvertised on -
 In the standard Lambda cold dark matter (Lambda-CDM) cosmology, galaxies grow by gradually accreting material and through mergers with other galaxies. This scenario successfully explains many large-scale cosmic structures, yet it struggles to account for the existence of numerous massive spiral galaxies in the local Universe that lack a prominent central bulge, pure disc systems, in the local Universe. Understanding how these galaxies form and survive is also essential for placing our own Galaxy, the Milky Way, into context, as it also hosts a low-mass bulge. In this study, we analyse 22Advertised on
In the standard Lambda cold dark matter (Lambda-CDM) cosmology, galaxies grow by gradually accreting material and through mergers with other galaxies. This scenario successfully explains many large-scale cosmic structures, yet it struggles to account for the existence of numerous massive spiral galaxies in the local Universe that lack a prominent central bulge, pure disc systems, in the local Universe. Understanding how these galaxies form and survive is also essential for placing our own Galaxy, the Milky Way, into context, as it also hosts a low-mass bulge. In this study, we analyse 22Advertised on