We analyze the spectral asymmetry of Stokes V (circularly polarized) profiles of an individual network patch in the quiet Sun observed by Sunrise/IMaX. At a spatial resolution of 0".15-0".18, the network elements contain substructure which is revealed by the spatial distribution of Stokes V asymmetries. The area asymmetry between the red and blue lobes of Stokes V increases from nearly zero at the core of the structure to values close to unity at its edges (single-lobed profiles). Such a distribution of the area asymmetry is consistent with magnetic fields expanding with height, i.e., an expanding magnetic canopy (which is required to fulfill pressure balance and flux conservation in the solar atmosphere). Inversion of the Stokes I and V profiles of the patch confirms this picture, revealing a decreasing field strength and increasing height of the canopy base from the core to the periphery of the network patch. However, the non-roundish shape of the structure and the presence of negative area and amplitude asymmetries reveal that the scenario is more complex than a canonical flux tube expanding with height surrounded by downflows.
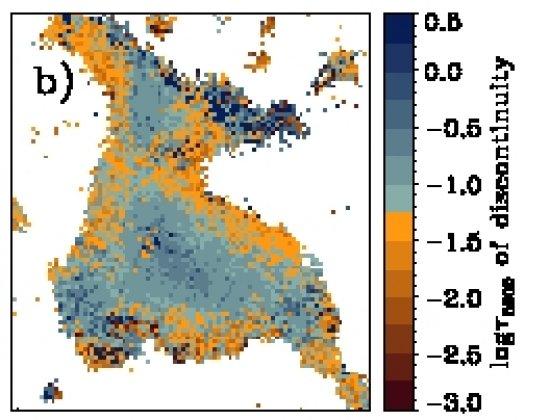
Logarithm of the optical depth of the discontonuity between the magnetic and the non magnetic atmosphere (i.e. the base of the canopy). Large positive numbers mean deep in the atmosphere while large negative numbers are higher layers of the atmosphere. Th
Advertised on
References
2012, ApJ, 758, 40L