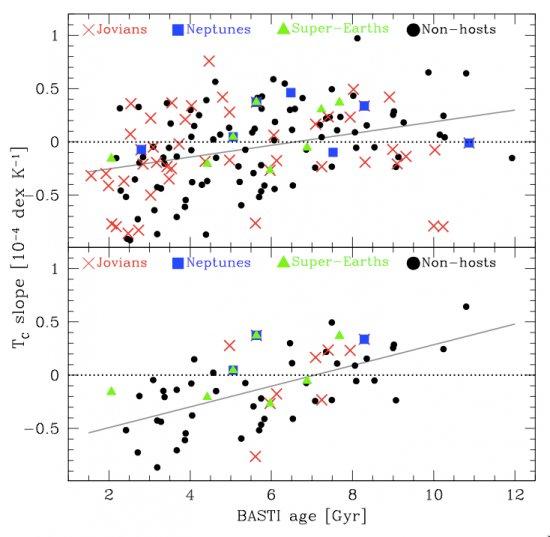
We explore a sample of 148 solar-like stars to search for a possible correlation between the slopes of the abundance trends versus condensation temperature (known as the Tc slope) with stellar parameters and Galactic orbital parameters in order to understand the nature of the peculiar chemical signatures of these stars and the possible connection with planet formation. We find that the Tc slope significantly correlates (at more than 4σ) with the stellar age and the stellar surface gravity (see Figure 1). We also find tentative evidence that the Tc slope correlates with the mean galactocentric distance of the stars (Rmean), suggesting that those stars that originated in the inner Galaxy have fewer refractory elements relative to the volatiles. While the average Tc slope for planet-hosting solar analogs is steeper than that of their counterparts without planets, this difference probably reflects the difference in their age and Rmean. We conclude that the age and probably the Galactic birth place are determinant to establish the star’s chemical properties. Old stars (and stars with inner disk origin) have a lower refractory-to-volatile ratio.
Tc slopes versus ages for the full sample (top panel) and for the solar analogs (bottom panel). Gray solid lines provide linear fits to the data points.
Advertised on
References