It may interest you
-
 An international team of astronomers, including researchers from the IAC, have performed a unique cosmic test - measuring the mass of an ancient star using two entirely different methods, finding agreement to within just 1.4%. This result marks a milestone in our ability to determine the ages of old stars and use them as living fossils to study the Milky Way’s distant past. The team analysed the red giant in the binary system KIC 10001167 using two independent approaches: firstly, by measuring the brightness and radial velocity variations due to the orbital motion of the binary, and secondlyAdvertised on
An international team of astronomers, including researchers from the IAC, have performed a unique cosmic test - measuring the mass of an ancient star using two entirely different methods, finding agreement to within just 1.4%. This result marks a milestone in our ability to determine the ages of old stars and use them as living fossils to study the Milky Way’s distant past. The team analysed the red giant in the binary system KIC 10001167 using two independent approaches: firstly, by measuring the brightness and radial velocity variations due to the orbital motion of the binary, and secondlyAdvertised on -
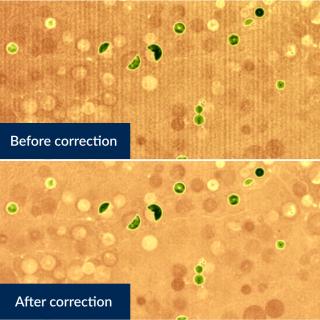 The European Patent Office (EPO) has granted the IAC a patent on an invention developed within IACTEC-Space . This technology improves the quality of images obtained by high-performance cameras under the demanding conditions found in space. The effectiveness of this technology has already been tested on three space missions, applying it to the DRAGO (Demonstrator for Remote Analysis of Ground Observations) cameras, developed at the IAC for Earth observation from space. Carlos Colodro, electronics engineer at IACTEC-Space and the main person responsible for this development, comments thatAdvertised on
The European Patent Office (EPO) has granted the IAC a patent on an invention developed within IACTEC-Space . This technology improves the quality of images obtained by high-performance cameras under the demanding conditions found in space. The effectiveness of this technology has already been tested on three space missions, applying it to the DRAGO (Demonstrator for Remote Analysis of Ground Observations) cameras, developed at the IAC for Earth observation from space. Carlos Colodro, electronics engineer at IACTEC-Space and the main person responsible for this development, comments thatAdvertised on -
 The Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias (IAC) has received a visit from Robert P. Kirshner, Executive Director of the Thirty Meter Telescope International Observatory (TIO) . During his stay at the IAC headquarters in La Laguna, he was welcomed by the center’s director, Valentín Martínez Pillet, and by the deputy director, Eva Villaver Sobrino, along with other members of the research institute. During his visit, he was able to learn firsthand about the institution’s scientific and technological capabilities and gave a colloquium titled The Thirty Meter Telescope and Science of the FutureAdvertised on
The Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias (IAC) has received a visit from Robert P. Kirshner, Executive Director of the Thirty Meter Telescope International Observatory (TIO) . During his stay at the IAC headquarters in La Laguna, he was welcomed by the center’s director, Valentín Martínez Pillet, and by the deputy director, Eva Villaver Sobrino, along with other members of the research institute. During his visit, he was able to learn firsthand about the institution’s scientific and technological capabilities and gave a colloquium titled The Thirty Meter Telescope and Science of the FutureAdvertised on