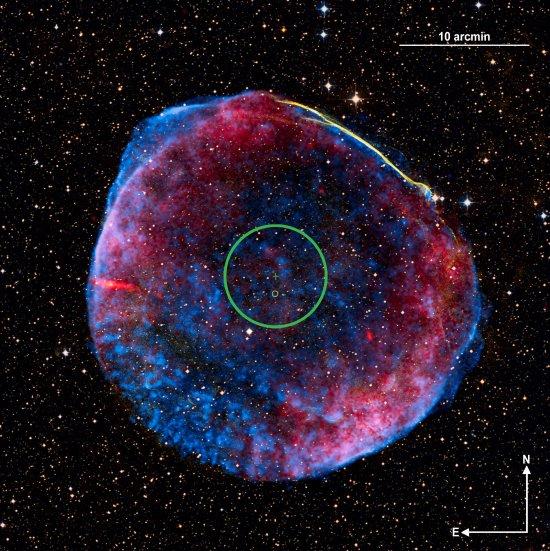
Type-Ia supernovae are thought to occur when a white dwarf made of carbon and oxygen accretes sufficient mass to trigger a thermonuclear explosion. The accretion could be slow, from an unevolved (main-sequence) or evolved (subgiant or giant) star (the single-degenerate channel), or rapid, as the primary star breaks up a smaller orbiting white dwarf (the double-degenerate channel). A companion star will survive the explosion only in the single-degenerate channel. Both channels might contribute to the production of type-Ia supernovae, but the relative proportions of their contributions remain a fundamental puzzle in astronomy. Previous searches for remnant companions have revealed one possible case for SN1572, although that has been questioned. More recently, observations have restricted surviving companions to be small, main-sequence stars, ruling out giant companions but still allowing the single-degenerate channel. Here we report the results of a search for surviving companions of the progenitor of SN1006. None of the stars within 4arc minutes of the apparent site of the explosion is associated with the supernova remnant, and we can firmly exclude all giant and subgiant stars from being companions of the progenitor. In combination with previous results, our findings indicate that fewer than 20 per cent of type-Ia supernovae occur through the single-degenerate channel.
The remnant of the SN1006. The surveyed area is indicated by the large green circle. The centre of the survey (the centroid of the X-ray emission) is marked with a green cross, and that of the Ha emission, by the small yellow circle. This is a composite i
Advertised on