Recently, Delgado-Inglada and collaborators have shown that low-mass (between one and three times the mass of the Sun) planetary nebulae are rich in oxygen, but the standard theoretical models do not predict this. In this work we explain this phenomenon for the first time using theoretical models of nucleosynthesis (production of chemical elements in the interiors of stars) in their precursor AGB stars, which include convective processes, (which transport chemical elements created in the interior to the surface of the star) more efficient than in the standard models. This discovery calls into question the traditional role of planetary nebulae as indicators of metallicity, which is the term used to cover the abundance of the elements which are heavier than hydrogen and helium initially present in the Universe, because now it has been confirmed theoretically that they are intrinsically rich in oxygen. The abundance of oxygen has been used historically to study the differences in the metallicity of our Galaxy and those of other nearby galaxies. In its place, this work confirms that other elements which are not so affected by stellar evolution, such as argon or chlorine should be used as indicators of metallicity. In the future, it will be necessary to use the predictions of these new models to analyse in detail the effect of these oxygen producing stars on the models of chemical evolution of galaxies; in fact they may have an important effect on the characteristic time scales for the formation of the majority of the stars in galaxies.
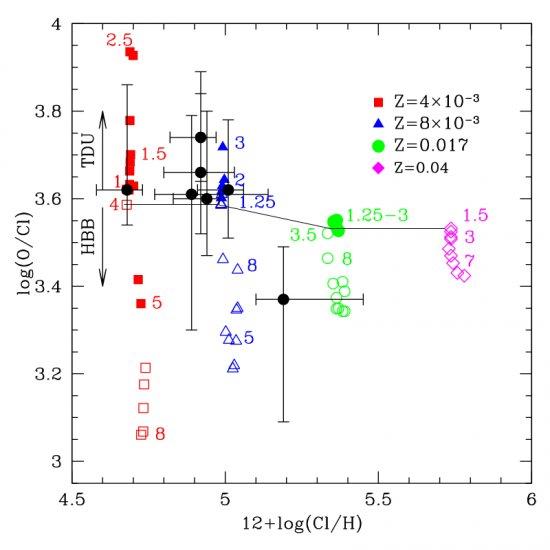
Oxygen and chlorine abundances in low-mass planetary nebulae (PNe) (black dots, from Delgado-Inglada et al. 2015) versus the new AGB model predictions for different masses (a few relevant masses are marked) and metallicities. The new models predict that O
Advertised on
References