Microquasars are compact binary stars (a normal very massive star and a compact object), which have an accretion disk around the compact object and an intense and variable radio emission, normally as bipolar jets (symmetric jets of matter in opposite directions). The unusual characteristic of the discovered microquasar in M81 is that the speed of the ejected material is close to the speed of light (that is known as relativistic jets), with a measured velocity of 17% that of light. The main properties of this microquasar all point to a black hole accreting at rates far exceeding the critical rate (there is a theoretical limit to the accretion rate, known as the Eddington limit). This type of black holes “disguise” themselves as supersoft X-ray sources that are normally thought as white dwarfs and the discovery shows observationally what happens if a black hole devours way too much. For this reason the scientists are suggesting this object to be a black hole with supercritical accretion (above the Eddington limit). The possible existence of this type of “superaccreting” black hole had been a source of speculation and research for years, and this result points to a first evidence of its existence.
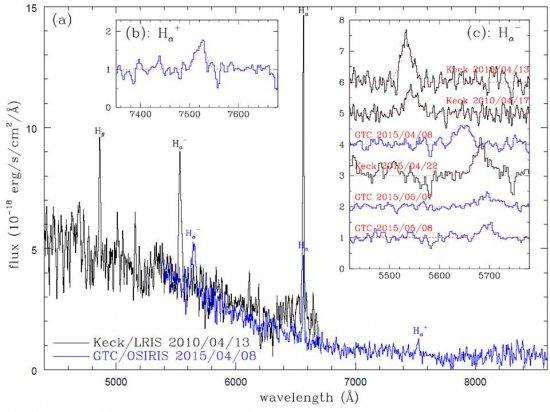
Keck and GTC spectra for the microquasar ULS-1 in M81. (a) Labeled over the lines are the broad Balmer lines (Hα and Hβ), the very broad blue-shifted H-α at 564.8 nm and roughly symmetric red-shifted H+α at 752.4 nm. The power-law like continuum and the b
Advertised on
References