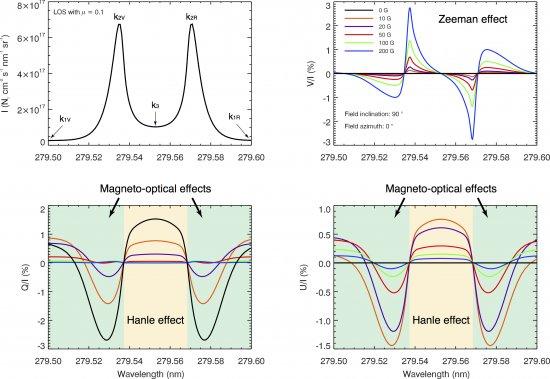
The polarization of the Mg II k line at 279.5 nm encodes valuable information on the magnetic field of the upper solar chromosphere, where this strong resonance line originates. We have developed a novel radiative transfer code which allows us to account for scattering polarization and the Hanle and Zeeman effects, as well as partial frequency redistribution (PRD) phenomena (i.e., correlation effects between the incoming and outgoing photons in the scattering events). This non-LTE code, which treats the atomic system and the polarized radiation field quantum-mechanically, has been applied to calculate the Stokes profiles that emerge from given models of the solar chromosphere considering various magnetic field configurations. The Hanle effect is the magnetic-field-induced modification of the linear polarization produced by scattering processes in a spectral line. Before this investigation, it was thought that the wings of the linear polarization profiles are insensitive to the presence of a magnetic field, and that the magnetic sensitivity of strong chromospheric lines, like the Mg II k line, is restricted to the circular polarization induced by the Zeeman effect and, via the Hanle effect, to the core of the linear polarization profiles. We have discovered that in strong resonance lines for which PRD effects are significant, like Mg II k, the magneto-optical terms of the Stokes-vector transfer equation introduce a very significant magnetic sensitivity in the wings of the linear polarization profiles. This hitherto unnoticed sensitivity to both weak (around 5 G) and stronger magnetic fields expands the scientific interest of the Mg II k line polarization as a diagnostic tool for probing the magnetism of the enigmatic solar chromosphere, both in quiet and active regions of the Sun. The second flight of the Chromospheric LAyer Spectro-Polarimeter (CLASP) will be dedicated to observe the wavelength variation of the Stokes profiles across the Mg II h & k lines. The first flight of the CLASP sounding rocket experiment, proposed by NASA, JAXA and the IAC, took place on September 3, 2015. This very successful international project provided the first measurement of the polarization in an ultraviolet line of the solar disk radiation (hydrogen Lyman-alpha at 121.6 nm), and the first empirical exploration of the geometrical complexity and magnetic field of the chromosphere-corona transition region of the Sun.
The Stokes profiles of the Mg II k line calculated in a semi-empirical model of the solar atmosphere, in the absence (black curves) and in the presence (coloured curves) of a horizontal magnetic field with zero azimuth (i.e., on the plane defined by the l
Advertised on
References