We present a visual determination of the number of bright points (BPs) existing in the quiet Sun, which are structures thought to trace intense kG magnetic concentrations. The measurement is based on a 0farcs1 angular resolution G-band movie obtained with the Swedish Solar Telescope at the solar disk center. We find 0.97 BPs Mm-2, which is a factor 3 larger than any previous estimate. It corresponds to 1.2 BPs per solar granule. Depending on the details of the segmentation, the BPs cover between 0.9% and 2.2% of the solar surface. Assuming their field strength to be 1.5 kG, the detected BPs contribute to the solar magnetic flux with an unsigned flux density between 13 G and 33 G. If network and inter-network regions are counted separately, they contain 2.2 BPs Mm-2 and 0.85 BPs Mm-2, respectively.
Advertised on
References
(2010) Magnetic bright points in the quiet Sun. ApJ, 715, L26
It may interest you
-
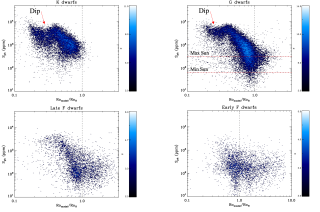 It’s been decades since the need to study other stars to understand the past, present and future of the Sun was realized. One important aspect that has been investigated is the magnetic activity of stars for which we cannot fully grasp the mechanisms involved. Indeed, the origin of stellar magnetic cycles or the dependence of the magnetic activity on the stellar properties are not completely understood. This knowledge improves not only our understanding of the physics involved in stellar evolution but also affects the study of the Sun to better predict high-energy events and the betterAdvertised on
It’s been decades since the need to study other stars to understand the past, present and future of the Sun was realized. One important aspect that has been investigated is the magnetic activity of stars for which we cannot fully grasp the mechanisms involved. Indeed, the origin of stellar magnetic cycles or the dependence of the magnetic activity on the stellar properties are not completely understood. This knowledge improves not only our understanding of the physics involved in stellar evolution but also affects the study of the Sun to better predict high-energy events and the betterAdvertised on -
 The most massive stars in the universe are often born and evolve in binary and multiple systems — that is, in pairs or groups bound by their mutual gravity. Understanding how they interact with each other is key to explaining everything from their formation to the impact they have on the galaxies they inhabit. The MONOS project (Multiplicity Of Northern O-type Spectroscopic systems) aims to study these systems in the northern sky, combining spectroscopic observations (which analyze light split into its component colors to measure stellar velocities and physical properties) with photometryAdvertised on
The most massive stars in the universe are often born and evolve in binary and multiple systems — that is, in pairs or groups bound by their mutual gravity. Understanding how they interact with each other is key to explaining everything from their formation to the impact they have on the galaxies they inhabit. The MONOS project (Multiplicity Of Northern O-type Spectroscopic systems) aims to study these systems in the northern sky, combining spectroscopic observations (which analyze light split into its component colors to measure stellar velocities and physical properties) with photometryAdvertised on -
 In the standard cosmological model (𝜦CDM), galaxies are merely the visible "tips of the icebergs," residing within massive, invisible cocoons of dark matter known as haloes. While these haloes dictate the evolution and motion of galaxies, measuring their true size and mass has long been one of the most challenging tasks in astrophysics. A new study published in Astronomy & Astrophysics by Claudio Dalla Vecchia and Ignacio Trujillo from the Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias (IAC) proposes a breakthrough: a physically motivated definition of a galaxy’s edge that acts as a precision "ruler"Advertised on
In the standard cosmological model (𝜦CDM), galaxies are merely the visible "tips of the icebergs," residing within massive, invisible cocoons of dark matter known as haloes. While these haloes dictate the evolution and motion of galaxies, measuring their true size and mass has long been one of the most challenging tasks in astrophysics. A new study published in Astronomy & Astrophysics by Claudio Dalla Vecchia and Ignacio Trujillo from the Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias (IAC) proposes a breakthrough: a physically motivated definition of a galaxy’s edge that acts as a precision "ruler"Advertised on