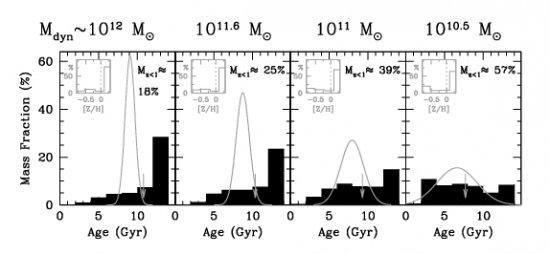
The abundance ratios between key elements such as iron and α-process elements carry a wealth of information on the star formation history (SFH) of galaxies. So far, simple chemical evolution models have linked [α/Fe ] with the SFH time-scale, correlating large abundance ratios with short-lived SFH. The incorporation of full spectral fitting to the analysis of stellar populations allows for a more quantitative constraint between [α/Fe ] and the SFH. In this letter, we provide, for the first time, an empirical correlation between [α/Fe ] (measured from spectral indices) and the SFH (determined via a non-parametric spectral-fitting method). We offer an empirical version of the iconic outline of Thomas et al., relating star formation time-scale with galaxy mass, although our results suggest, in contrast, a significant population of old (≳10 Gyr) stars even for the lowest mass ellipticals (M/dyn ˜ 3 × 1010 Msun). In addition, the abundance ratio is found to be strongly correlated with the time to build up the stellar component, showing that the highest [α/Fe ] (≳+0.2) are attained by galaxies with the shortest half-mass formation time (≲2 Gyr), or equivalently, with the smallest (≲40 per cent) fraction of populations younger than 10 Gyr. These observational results support the standard hypothesis that star formation incorporates the Fe-enriched interstellar medium into stars, lowering the high abundance ratio of the old populations.
Variation of the star formation history with respect to dynamical mass (each panel representing a mass bin as given in Table 2). Sketchy (theoretical) SFHs, plotted as grey Gaussian curves, are superimposed over the detailed (empirical) SFH histograms (bl
Advertised on
References