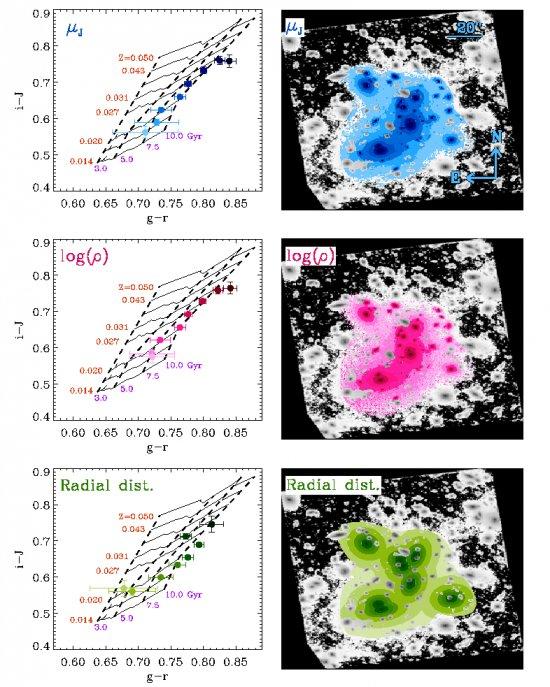
The ultra-deep multiwavelength Hubble Space Telescope Frontier Fields coverage of the Abell Cluster 2744 is used to derive the stellar population properties of its intracluster light (ICL). The restframe colors of the ICL of this intermediate redshift (z = 0.3064) massive cluster are bluer (g – r = 0.68 ± 0.04; i – J = 0.56 ± 0.01) than those found in the stellar populations of its main galaxy members (g – r = 0.83 ± 0.01; i – J = 0.75 ± 0.01). Based on these colors, we derive the following mean metallicity Z = 0.018 ± 0.007 for the ICL. The ICL age is 6 ± 3 Gyr younger than the average age of the most massive galaxies of the cluster. The fraction of stellar mass in the ICL component comprises at least 6% of the total stellar mass of the galaxy cluster. Our data are consistent with a scenario where the bulk of the ICL of A2744 has been formed relatively recently (z < 1). The stellar population properties of the ICL suggest that this diffuse component is mainly the result of the disruption of infalling galaxies with similar characteristics in mass (M*~ 3 × 10^10 Msolar) and metallicity than our own Milky Way. The amount of ICL mass in the central part of the cluster (<400 kpc) is equivalent to the disruption of 4-6 Milky-Way-type galaxies.
Figure caption: Left panels show the i − J vs. g − r diagrams for three different parameters: surface brightness in restframe J (μJ, blue), the logarithm of the stellar mass density (log (ρ), pink), and the radial distance to the most massive galaxies of
Advertised on
References