Utilizando modelos semiempíricos de los espectros de fotoabsorción de varios fullerenos individuales (C_80, C_240, C_320 y C_540) predecimos transiciones en la región de la banda difusa más intensa del medio interestelar a 4430 A que podrían explicar su origen, hasta ahora desconocido. Estos modelos también presentan una alta densidad de transiciones en el ultravioleta que reproducen el denominado "bump" a 2175 A en la curva de extinción del medio interestelar (Iglesias-Groth 2004). Parece que los fullerenos podrían ser responsables de dos de los mayores rasgos de la absorción interestelar. Haciendo uso de las secciones eficaces teóricas y de los datos empíricos estimamos que la abundancia de fullerenos es de 0.05 moléculas por millón de átomos de hidrógeno en regiones del medio interestelar con índice de exceso de color E(B-V)~ 1.0.
Advertised on
It may interest you
-
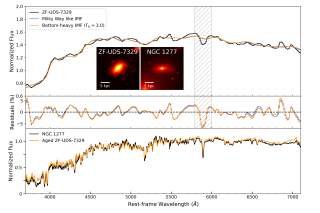 Observations made with the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) have revealed a larger-than-expected number of massive galaxies when the Universe was still young. The focus of this study is precisely one of these galaxies, ZF-UDS-7329. It is a very compact object, and its spectrum suggests that it formed at a very early stage, when the Universe was around 2 billion years old. According to theoretical predictions, these objects first formed a generation of stars at the center of their dark matter halos and subsequently grew by merging with other halos. However, due to the random nature of theseAdvertised on
Observations made with the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) have revealed a larger-than-expected number of massive galaxies when the Universe was still young. The focus of this study is precisely one of these galaxies, ZF-UDS-7329. It is a very compact object, and its spectrum suggests that it formed at a very early stage, when the Universe was around 2 billion years old. According to theoretical predictions, these objects first formed a generation of stars at the center of their dark matter halos and subsequently grew by merging with other halos. However, due to the random nature of theseAdvertised on -
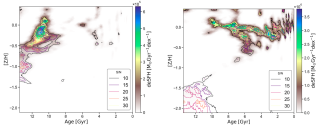 Research on the formation, origin, and evolution of the dichotomy between the thin and thick disk components of the Milky Way has been a major topic of study, as it is key to understanding how our Galaxy formed. However, this is not an easy task, since populations defined by their morphology or kinematics show a mixture of chemically distinct stellar populations. Age therefore becomes a fundamental parameter for understanding the evolution of the Galactic disk. Our goal is to derive the age and metallicity distributions of the thin and thick disks defined kinematically, in order to revealAdvertised on
Research on the formation, origin, and evolution of the dichotomy between the thin and thick disk components of the Milky Way has been a major topic of study, as it is key to understanding how our Galaxy formed. However, this is not an easy task, since populations defined by their morphology or kinematics show a mixture of chemically distinct stellar populations. Age therefore becomes a fundamental parameter for understanding the evolution of the Galactic disk. Our goal is to derive the age and metallicity distributions of the thin and thick disks defined kinematically, in order to revealAdvertised on -
 In the standard cosmological model (𝜦CDM), galaxies are merely the visible "tips of the icebergs," residing within massive, invisible cocoons of dark matter known as haloes. While these haloes dictate the evolution and motion of galaxies, measuring their true size and mass has long been one of the most challenging tasks in astrophysics. A new study published in Astronomy & Astrophysics by Claudio Dalla Vecchia and Ignacio Trujillo from the Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias (IAC) proposes a breakthrough: a physically motivated definition of a galaxy’s edge that acts as a precision "ruler"Advertised on
In the standard cosmological model (𝜦CDM), galaxies are merely the visible "tips of the icebergs," residing within massive, invisible cocoons of dark matter known as haloes. While these haloes dictate the evolution and motion of galaxies, measuring their true size and mass has long been one of the most challenging tasks in astrophysics. A new study published in Astronomy & Astrophysics by Claudio Dalla Vecchia and Ignacio Trujillo from the Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias (IAC) proposes a breakthrough: a physically motivated definition of a galaxy’s edge that acts as a precision "ruler"Advertised on