By Javier Pérez Barbuzano.
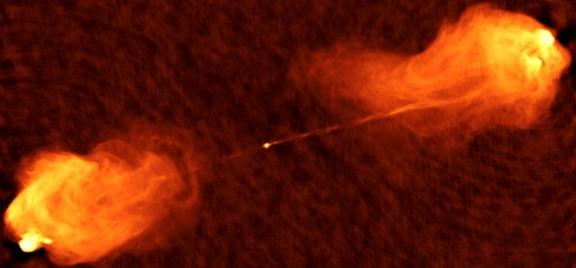
Cygnus A is an elliptical galaxy at around 600 million light years from the Earth, which has a supermassive black hole at its centre. It is one of the brightest sources of radio waves in the sky and featured in Contact, the famous science fiction novel by Carl Sagan which was made into a film. It has an active galactic nucleus which means that the black hole is “swallowing” material from its surroundings. When this occurs strong electromagnetic radiation is produced, as well as large jets of particles which are emitted from the galactic nucleus at a speed close to that of light, travelling beyond the edge of the galaxy and reaching three hundred thousand light years into the intergalactic medium.
This is the first time that polarimetric observations in the middle infrared region of the spectrum (1) have been made of the nucleus of an active galaxy. “The combination of the Gran Telescopio CANARIAS (GTC) and CanariCam offers unique capabilities for the observation of active galaxies using polarimetric techniques in the middle infrared” explains Enrique López Rodríguez, a researcher at the University of Texas in Austin (EE UU) and the first author of this study, published in the Astrophysical Journal. “There is no other comparable instrument of this kind, he stresses, and no such instruments are expected until the next decade, because the instruments which are being developed now cannot make polarimetric measurements”.
Polarimetry is the technique which studies the intensity and the orientation of electromagnetic waves. “If the observed radiation is polarized in a given sense and with a given dependence on wavelength we can obtain information about the physical mechanisms which produce the polarization. This technique helps us squeeze out the last drop of information from each photon picked up by the GTC” says López Rodríguez”. “Polarimetry” he adds lets us eliminate from the observations all the light which is not affected by the magnetic field in the active nucleus, so that we can filter out everything which comes from other sources, such as the galaxy itself, or background stars. This gives us a much higher contrast when we observe the jets and the dust in the galaxy, while studying the influence of the magnetic field on both of them”.
On the basis of these observations the astronomers have been able to detect that the plasma ejected from the active nucleus is spiraling around the magnetic field of the jet, which generates a type of radiation known as “synchrotron radiation”, produced by the rapid movement of electrons around magnetic fields. Although this phenomenon had been observed previously at other wavelengths, this is the first time it has been detected in the middle infrared, which has enabled us to confirm that the plasma in the jet of Cygnus A is highly confined by the effect of the magnetic field. These observations allow us to obtain information about the configuration of the magnetic field in the neighbourhood of the black hole (2), valuable information which cannot be directly observed.
A cosmic jigsaw
Astronomers classify Cygnus A as a radiogalaxy because it is one of the most powerful radio sources in the sky. It was observed for the first time in 1939 and it is named because it is the strongest radio source in the constellation of the Swan (latin name Cygnus). Nevertheless this galaxy emits radiation over the full range of the electromagnetic spectrum which makes it an ideal astronomical laboratory, and one of the favourite objects of astronomers, who have been making observations with diverse instruments and at different wavelengths, interpreting them to compose the pieces of a cosmic jigsaw which will let us understand better what is happening in that region of the universe.
Cygnus A has a very complex structure which includes a compact nucleus and opposed jets of matter emitted from the centre of the galaxy towards the edges, all shrouded in a mantle of dust with an irregular structure which is impenetrable to visible light. “It is a paradigm galaxy for studying the formation and evolution of jets, because the dust completely obscures the centre of the galaxy, so that we cannot detect well the light emitted by the jets” explains López Rodríguez. This is why the research team has used CanariCam, and instrument designed to detect infrared radiation, which is not blocked by interstellar dust.
The Gran Telescopio CANARIAS is uniquely equipped to make these observations. Thanks to its large primary mirror, which favours high spatial resolution, and the CanariCam instrument, which can observe in the middle infrared wavelength range, we can study the infrared radiation emitted by the galaxy. This emission comes from matter which is not hot enough to emit visible light, but are warm enough (around 220K, which is -53ºC) to emit infrared radiation. In addition the polarimetric capability of CanariCam gives an additional dimension of information with which astronomers can analyze to interpret different physical mechanisms.
Until now very little has been known about the polarization of the infrared radiation emitted by the supermassive black holes which are at the centres of the majority of galaxies. Astronomers hope that these, and other similar observations can provide new data which will help them to understand the mechanisms which cause the activity of these cosmic monsters, and their influence on the galaxies which they inhabit.
Notes:
[1] With the aim of explaining the dominant mechanism which polarizes the radiation from Cygnus A at infrared wavelengths this study presents polarimetric observations at high angular resolution (0.4 arcseconds) in the filters at 8.7mm and 11.6 mm, using the CanariCam instrument on the Gran Telescopio CANARIAS (GTC) of 10.4 metres diameter at the Roque de los Muchachos Observatory of the Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias on the island of La Palma (Spain).
[2] For Cygnus A, the 65% of polarization measured in the middle infrared is close to the theoretical máximum of 70% which indicates that there is a highly ordered magnetic field around the nucleus of Cygnus A.
Article: “Polarized mid-infrared synchrotron emission in the core of Cygnus A”, by E. Lopez-Rodríguez (University of Texas, EEUU), C. Packham (University of Texas, EEUU), C. Tadhunter (University of Sheffield, UK), R. Mason (Gemini Observatory, EE.UU), E. Perlman (Florida Institute of Technology, EE.UU), A. Alonso-Herrero (Instituto de Física de Cantabria-August G. Linares Senior Research Fellow), C. Ramos Almeida (IAC, ULL, Marie Curie Fellow), K. Ichikawa (Kyoto University, Japón), N. A. Levenson (Gemini Observatory, Chile), J. M. Rodríguez-Espinosa (IAC-ULL), C. A. Álvarez (ULL-GTC Project), E. A. Ramírez (Universidade de São Paulo, Brasil), and C. M. Telesco (University of Florida, EE.UU). 2014, ApJ 793 81.
DOI: http://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.1088/0004-637X/793/2/81?fromSearchPage=true
Contact:
Enrique López Rodríguez: Departamento de Física y Astronomía, Universidad de Texas, San Antonio (EE.UU). enrique.lopezrodriguez [at] utexas.edu (enrique[dot]lopezrodriguez[at]utexas[dot]edu)
Cristina Ramos Almeida (IAC): cra [at] iac.es
José Miguel Rodríguez Espinosa (IAC): jre [at] iac.es