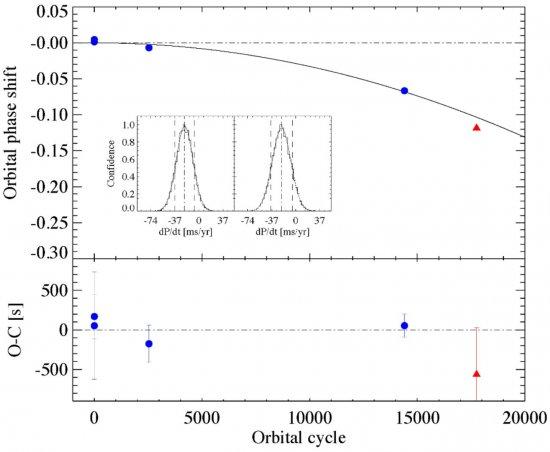
We present new medium-resolution spectroscopic observations of the black hole X-ray binary Nova Muscae 1991 taken with X-Shooter spectrograph installed at the 8.2-m VLT telescope. These observations allow us to measure the time of inferior conjunction of the secondary star with the black hole in this system that, together with previous measurements, yield an orbital period decay of (dP/dt)= −20.7±12.7 ms yr−1 (−24.5 ± 15.1 μs per orbital cycle). This is significantly faster than those previously measured in the other black hole X-ray binaries A0620-00 and XTE J1118+480. No standard black hole X-ray binary evolutionary model is able to explain this extremely fast orbital decay. At this rate, the secondary star would reach the event horizon (as given by the Schwarzschild radius of about 32 km) in roughly 2.7 Myr. This result has dramatic implications on the evolution and lifetime of black hole X-ray binaries.
Top panel: orbital phase shift at the time of the inferior conjunction (orbital phase 0), Tn, of the secondary star in the black hole X-ray binary Nova Muscae 1991 versus the orbital cycle number, n, folded on the best-fitting parabolic fit. The error bar
Advertised on
References