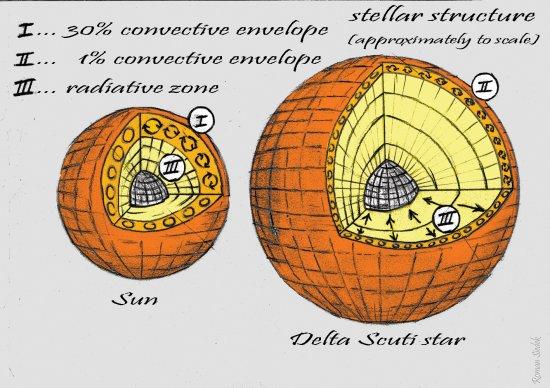
Delta Scuti (δ Sct) stars are opacity-driven pulsators with masses of 1.5-2.5M⊙, their pulsations resulting from the varying ionization of helium. In less massive stars such as the Sun, convection transports mass and energy through the outer 30 per cent of the star and excites a rich spectrum of resonant acoustic modes. Based on the solar example, withno firm theoretical basis, models predict that the convective envelope in δ Sct stars extends only about 1 per cent of the radius, but with sufficient energy to excite solar-like oscillations. This was not observed before the Kepler mission, so the presence of a convective envelope in the models has been questioned. Here we report the detection of solar-like oscillations in the δ Sct star HD 187547, implying that surface convection operates efficiently in stars about twice as massive as the Sun, as the ad hoc models predicted.
Advertised on
It may interest you
-
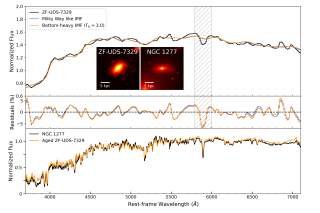 Observations made with the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) have revealed a larger-than-expected number of massive galaxies when the Universe was still young. The focus of this study is precisely one of these galaxies, ZF-UDS-7329. It is a very compact object, and its spectrum suggests that it formed at a very early stage, when the Universe was around 2 billion years old. According to theoretical predictions, these objects first formed a generation of stars at the center of their dark matter halos and subsequently grew by merging with other halos. However, due to the random nature of theseAdvertised on
Observations made with the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) have revealed a larger-than-expected number of massive galaxies when the Universe was still young. The focus of this study is precisely one of these galaxies, ZF-UDS-7329. It is a very compact object, and its spectrum suggests that it formed at a very early stage, when the Universe was around 2 billion years old. According to theoretical predictions, these objects first formed a generation of stars at the center of their dark matter halos and subsequently grew by merging with other halos. However, due to the random nature of theseAdvertised on -
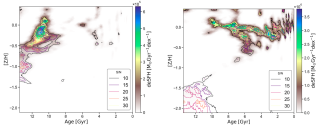 Research on the formation, origin, and evolution of the dichotomy between the thin and thick disk components of the Milky Way has been a major topic of study, as it is key to understanding how our Galaxy formed. However, this is not an easy task, since populations defined by their morphology or kinematics show a mixture of chemically distinct stellar populations. Age therefore becomes a fundamental parameter for understanding the evolution of the Galactic disk. Our goal is to derive the age and metallicity distributions of the thin and thick disks defined kinematically, in order to revealAdvertised on
Research on the formation, origin, and evolution of the dichotomy between the thin and thick disk components of the Milky Way has been a major topic of study, as it is key to understanding how our Galaxy formed. However, this is not an easy task, since populations defined by their morphology or kinematics show a mixture of chemically distinct stellar populations. Age therefore becomes a fundamental parameter for understanding the evolution of the Galactic disk. Our goal is to derive the age and metallicity distributions of the thin and thick disks defined kinematically, in order to revealAdvertised on -
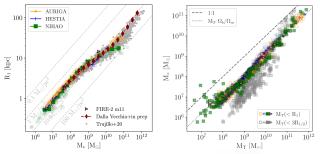 Measuring galaxy sizes is essential for understanding how they were formed and evolved across time. However, traditional methods based on l ight concentration or isophotal densities often lack a clear physical meaning. A recent study from Trujillo+20 explores a more physically motivated definition: the radius R 1, where the stellar surface density falls to 1 solar masses per parsec square —roughly the threshold for gas to form stars in galaxies like the Milky Way. In this work, Arjona-Gálvez+25 uses over 1,000 galaxies from several state-of-the-art cosmological simulations (AURIGA, HESTIAAdvertised on
Measuring galaxy sizes is essential for understanding how they were formed and evolved across time. However, traditional methods based on l ight concentration or isophotal densities often lack a clear physical meaning. A recent study from Trujillo+20 explores a more physically motivated definition: the radius R 1, where the stellar surface density falls to 1 solar masses per parsec square —roughly the threshold for gas to form stars in galaxies like the Milky Way. In this work, Arjona-Gálvez+25 uses over 1,000 galaxies from several state-of-the-art cosmological simulations (AURIGA, HESTIAAdvertised on