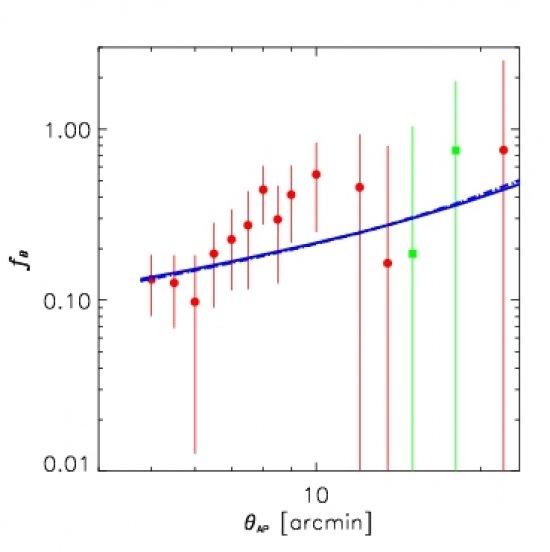
The total baryon content in the Universe is a well-defined quantity, in addition to being one of the most important cosmological parameters. A variety of observations (CMB, Ly-alpha forest, Big Bang nucleosynthesis) indicate that all baryons amount to around 4% of the total matter-energy content of the Universe. However, in the local Universe the contribution of all the observed components represents around 2% of the total. Therefore, half of the baryons in the local Universe remain elusive. In this article we have presented measurements of the kinematic Sunyaev-Zel’dovich effect in Planck data towards BOSS galaxies, that are compatible with the detection of all baryons in and around these galaxies (including the missing baryons), which represents around half of the total baryons in the Universe out to z=0.12, the maximum redshift sampled by these galaxies.
Each point represents one individual measurement of the baryon fraction relative to the Universal baryon content, at a given distance around BOSS galaxies. Red points correspond to detections, positive signal with its corresponding error bar, whereas gree
Advertised on
References