We find a distinct stellar population in the counterrotating and kinematically decoupled core of the isolated massive elliptical galaxy NGC 1700. Coinciding with the edge of this core, we find a significant change in the slope of the gradient of various representative absorption line indices. Our age estimate for this core is markedly younger than the main body of the galaxy. We find lower values for the age, metallicity, and Mg/Fe abundance ratio in the center of this galaxy when we compare them with other isolated elliptical galaxies with similar velocity dispersion. We discuss the different possible scenarios that might have lead to the formation of this younger kinematically decoupled structure and conclude that, in light of our findings, the ingestion of a small stellar companion on a retrograde orbit is the most favored.
Advertised on
References
2011, ApJ, 732L, 33K
It may interest you
-
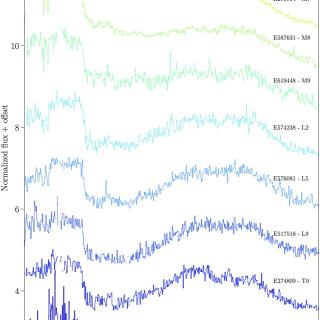 The Near-Infrared Spectrometer and Photometer (NISP) on board the Euclid space mission has obtained near-infrared (NIR) spectra of millions of objects, including hundreds of ultracool dwarfs (UCDs). Euclid observations retrieve images and slitless spectra simultaneously. This observing mode marks a new era in the discovery of new objects, such as L- and T-type dwarfs, which can be found from direct identification through the H2O and CH4 absorption bands. NISP spectral resolution (R ∼ 450) is enough to classify the objects by the spectral type using known standard templates. Q1 provided moreAdvertised on
The Near-Infrared Spectrometer and Photometer (NISP) on board the Euclid space mission has obtained near-infrared (NIR) spectra of millions of objects, including hundreds of ultracool dwarfs (UCDs). Euclid observations retrieve images and slitless spectra simultaneously. This observing mode marks a new era in the discovery of new objects, such as L- and T-type dwarfs, which can be found from direct identification through the H2O and CH4 absorption bands. NISP spectral resolution (R ∼ 450) is enough to classify the objects by the spectral type using known standard templates. Q1 provided moreAdvertised on -
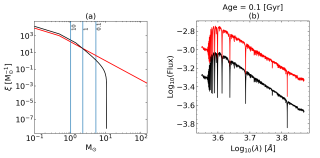 We present, for the first time, model spectra of single-age, single-metallicity stellar populations computed with the E-MILES evolutionary synthesis code incorporating an environment-dependent, variable galaxy-wide initial mass function (gwIMF). This gwIMF, calculated using the GalIMF code, is rooted in the integrated galactic initial mass function (IGIMF) theory, which predicts IMF variations as a function of the star formation rate and the metallicity. By coupling these two codes, we generated a comprehensive library of single-burst stellar population spectra uniquely sensitive to gwIMFAdvertised on
We present, for the first time, model spectra of single-age, single-metallicity stellar populations computed with the E-MILES evolutionary synthesis code incorporating an environment-dependent, variable galaxy-wide initial mass function (gwIMF). This gwIMF, calculated using the GalIMF code, is rooted in the integrated galactic initial mass function (IGIMF) theory, which predicts IMF variations as a function of the star formation rate and the metallicity. By coupling these two codes, we generated a comprehensive library of single-burst stellar population spectra uniquely sensitive to gwIMFAdvertised on -
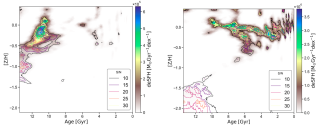 Research on the formation, origin, and evolution of the dichotomy between the thin and thick disk components of the Milky Way has been a major topic of study, as it is key to understanding how our Galaxy formed. However, this is not an easy task, since populations defined by their morphology or kinematics show a mixture of chemically distinct stellar populations. Age therefore becomes a fundamental parameter for understanding the evolution of the Galactic disk. Our goal is to derive the age and metallicity distributions of the thin and thick disks defined kinematically, in order to revealAdvertised on
Research on the formation, origin, and evolution of the dichotomy between the thin and thick disk components of the Milky Way has been a major topic of study, as it is key to understanding how our Galaxy formed. However, this is not an easy task, since populations defined by their morphology or kinematics show a mixture of chemically distinct stellar populations. Age therefore becomes a fundamental parameter for understanding the evolution of the Galactic disk. Our goal is to derive the age and metallicity distributions of the thin and thick disks defined kinematically, in order to revealAdvertised on