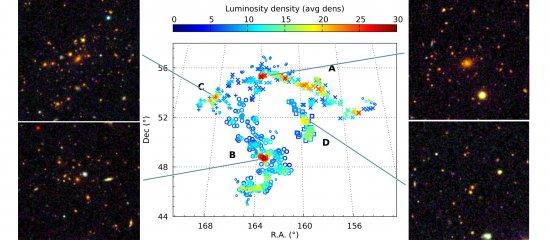
Superclusters are the largest over-dense, relatively isolated systems in the cosmic web. They provide us invaluable information about the large-scale structure formation at different cosmic epochs, as well as they are excellent places for understanding galaxy evolution in detail. Thanks to the new SDSS-III data, we can extend our knowledge of superclusters to the redshift range above z=0.4. We used data from the twelfth data release of the Sloan Digital Sky Survey (SDSS). Using a sample of more than 500,000 galaxies up to z~0.8, we reconstructed the large-scale luminosity-density field and we used it to detect large-scale over-dense regions. The largest structure in this field, that we called the BOSS Great Wall (BGW), is located at z~0.47 and consisted of two walls with diameters ~180 h-1 Mpc each. The BGW is the larger in volume and diameter structure than any previously known superclusters. Other known superclusters, like the Sloan Great Wall or Laniakea are almost half the size of the BGW. In addition, the BGW contains 830 galaxies and the total mass of our system is at least two times higher than any other superclusters. These characteristics make the BOSS Great Wall the richest, and largest system found in the Universe, and one of the most massive structures ever known.
Distributions of 830 galaxies in the BOSS Great Wall (BGW). The colour scale shows the local environmental density in terms of mean densities for each galaxy. With a total diameter of 271 h-1 Mpc and average redshift of 0.47 for its sources, this superclu
Advertised on
References