It may interest you
-
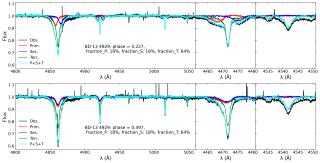 The most massive stars in the universe are often born and evolve in binary and multiple systems — that is, in pairs or groups bound by their mutual gravity. Understanding how they interact with each other is key to explaining everything from their formation to the impact they have on the galaxies they inhabit. The MONOS project (Multiplicity Of Northern O-type Spectroscopic systems) aims to study these systems in the northern sky, combining spectroscopic observations (which analyze light split into its component colors to measure stellar velocities and physical properties) with photometryAdvertised on
The most massive stars in the universe are often born and evolve in binary and multiple systems — that is, in pairs or groups bound by their mutual gravity. Understanding how they interact with each other is key to explaining everything from their formation to the impact they have on the galaxies they inhabit. The MONOS project (Multiplicity Of Northern O-type Spectroscopic systems) aims to study these systems in the northern sky, combining spectroscopic observations (which analyze light split into its component colors to measure stellar velocities and physical properties) with photometryAdvertised on -
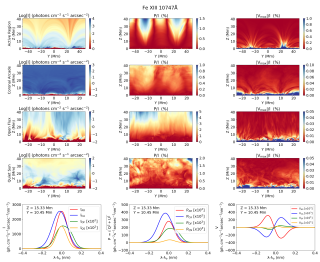 The solar corona—the outermost layer of the Sun’s atmosphere—is extremely hot and very low in density. One of the main challenges in solar physics is understanding why the corona reaches temperatures of over a million degrees. This heating is believed to be closely related to the Sun’s magnetic field. However, quantifying the coronal magnetic field is difficult because the light emitted by the corona is extremely faint, and its polarization signals, which encode the information on the magnetic field, are subtle. Thanks to recent advances in technology, telescopes like the Daniel K. InouyeAdvertised on
The solar corona—the outermost layer of the Sun’s atmosphere—is extremely hot and very low in density. One of the main challenges in solar physics is understanding why the corona reaches temperatures of over a million degrees. This heating is believed to be closely related to the Sun’s magnetic field. However, quantifying the coronal magnetic field is difficult because the light emitted by the corona is extremely faint, and its polarization signals, which encode the information on the magnetic field, are subtle. Thanks to recent advances in technology, telescopes like the Daniel K. InouyeAdvertised on -
 O ne of the key challenges in astronomy is to measure accurate distances to celestial objects. Knowing distances is crucial since it allows us to measure physical properties such as size, mass and luminosity. Since we can’t go out and use a tape-measure, a range of different approaches have been developed. Many of these approaches rely on using “standard candles”. Standard candles are objects (for example stars or supernovae) for which we know their intrinsic ”true” brightness. Once we know this, then their observed brightness compared to their intrinsic brightness gives us a distance to theAdvertised on
O ne of the key challenges in astronomy is to measure accurate distances to celestial objects. Knowing distances is crucial since it allows us to measure physical properties such as size, mass and luminosity. Since we can’t go out and use a tape-measure, a range of different approaches have been developed. Many of these approaches rely on using “standard candles”. Standard candles are objects (for example stars or supernovae) for which we know their intrinsic ”true” brightness. Once we know this, then their observed brightness compared to their intrinsic brightness gives us a distance to theAdvertised on
